1. Embedded Systems: The Brains of IoT Devices
Embedded systems are specialized computing systems intended to perform specific tasks within larger systems. They are small but powerful devices that form the backbone of IoT, acting as the “brains” behind smart devices.
Role of Embedded Systems in IoT
Device Control and Communication
Embedded systems empower the IoT devices with the capability of processing and also allowing interaction between other devices or cloud platforms. For example, an intelligent thermostat uses an embedded system in order to sense temperature, process user inputs and can control HVAC systems.
Energy Efficiency
Embedded systems are designed to function on resource-constrained environments, making them extremely energy-optimized. This becomes a crunch condition for most IoT battery-operated devices like wearables and remote sensors.
Customizable Functionality
Embedded systems can be tailored for specific applications, whether it’s monitoring industrial machinery, automating home appliances, or enabling autonomous vehicles.
Emerging Trends in Embedded Systems for IoT
Real-Time Processing: IoT applications demand real-time data processing, which is made possible by advanced microcontrollers and embedded operating systems.
Security Features: Modern embedded systems incorporate encryption and secure boot mechanisms to address IoT cybersecurity challenges.
In the following, businesses can create smarter, faster, and more reliable solutions to enhance user experience by adding the feature of an embedded system into IoT devices.
2. Wireless Sensor Networks: The Eyes and Ears of IoT
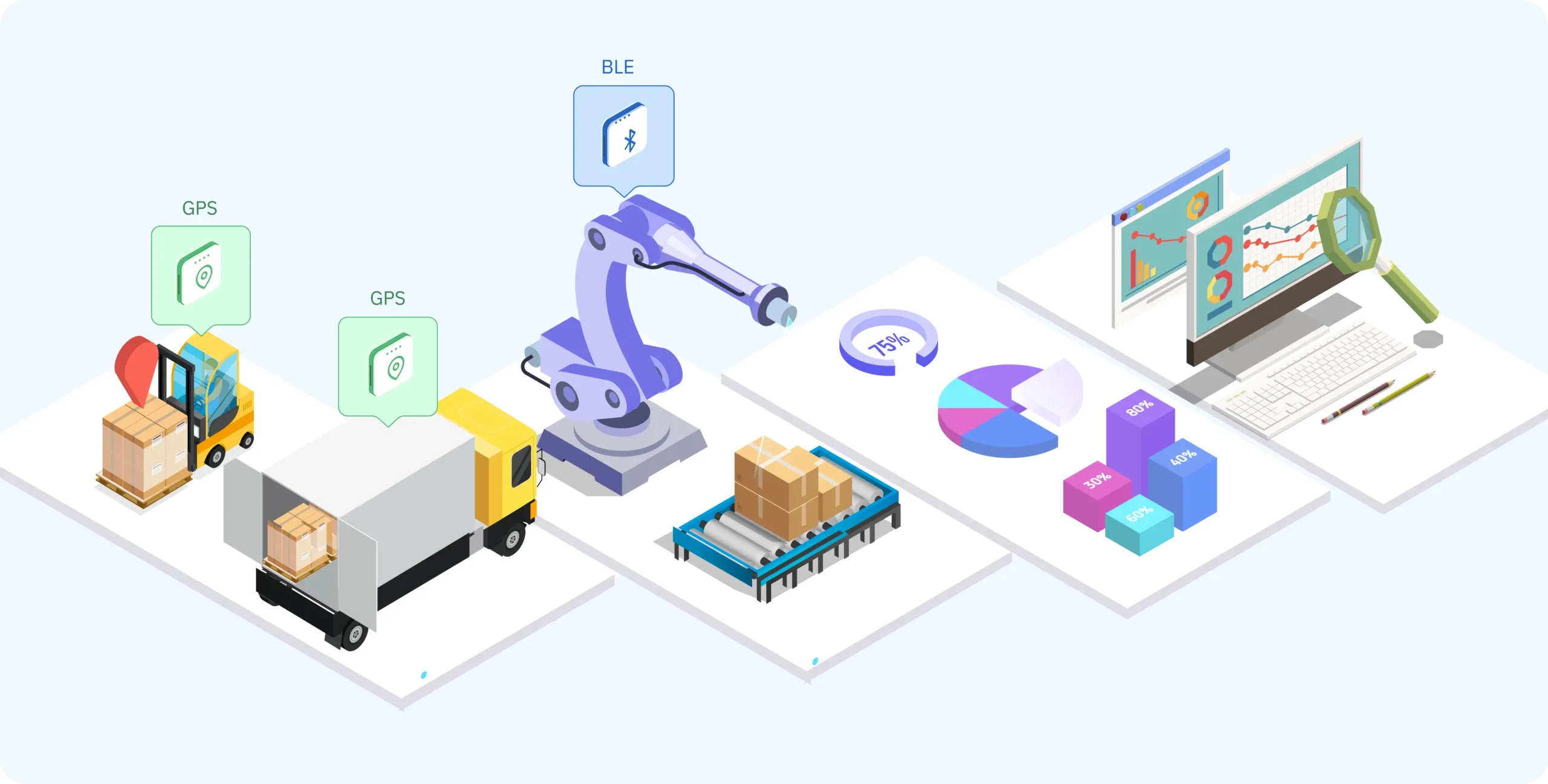
WSNs (wireless sensor networks) refer to sets of spatially distributed sensors that collect data and transfer it wirelessly to a central hub or cloud. These networks are an integral part of the IoT ecosystem and perform the role of “eyes and ears” in connected systems.
How WSNs Enable IoT
Data Collection
WSNs collect real-time data from the environment, like temperature, humidity, motion, and pressure. In an agricultural scenario, soil moisture sensors would monitor field conditions, sending this data back to the farmers in a WSN to enable precision farming.
Remote Monitoring
IoT applications use WSNs for remote monitoring in areas inaccessible or difficult to reach, such as offshore oil rigs or forested areas for wildfire detection.
Low-Power Connectivity
Applications of WSN in IoT
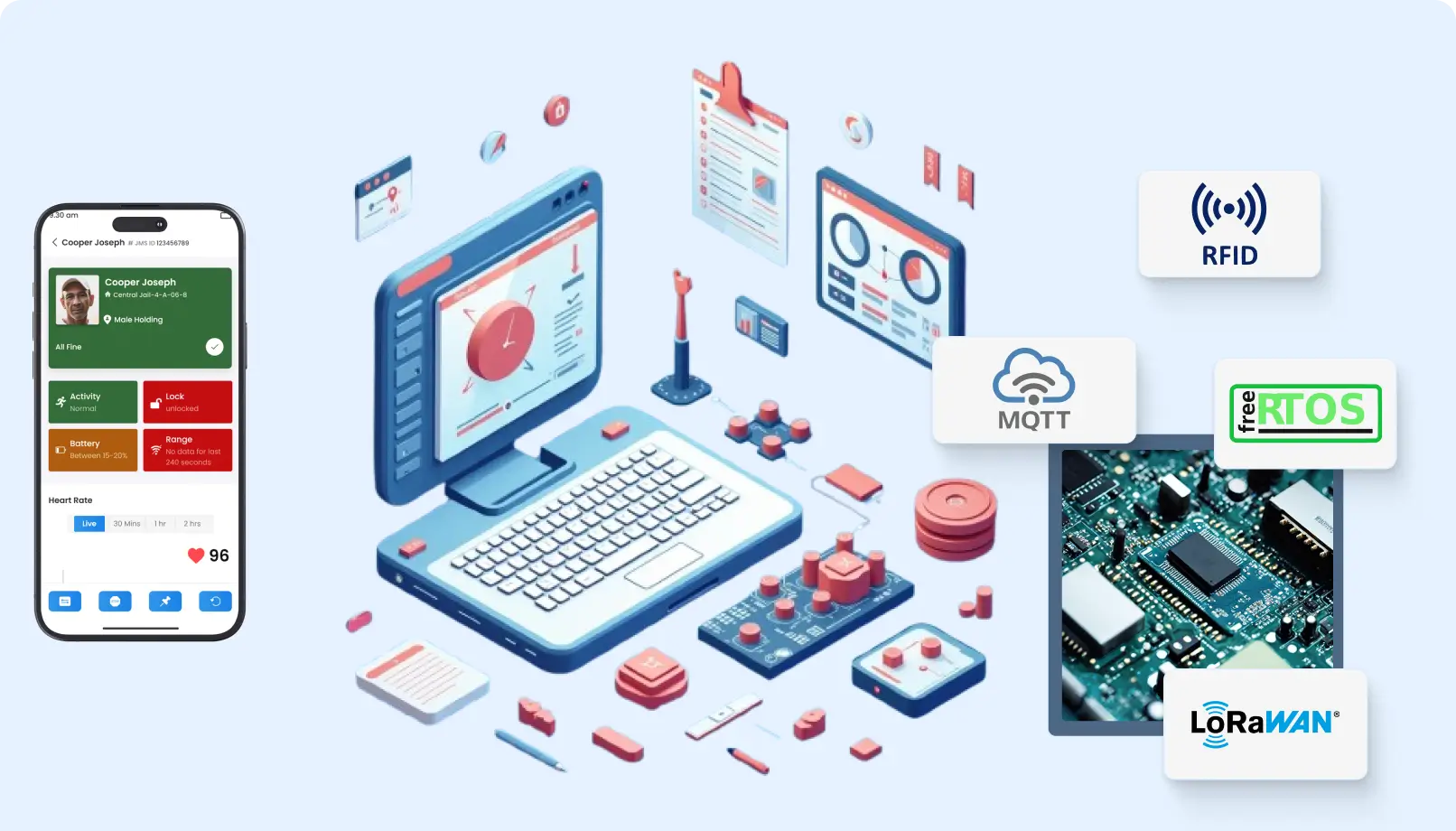
Health care: Wearable devices can monitor patients’ vital signs and send data to healthcare providers.
Smart Homes: Motion and occupancy sensors improve home automation and security.
IIoT: WSN enables real-time monitoring of machinery performance, which allows predictive maintenance.
WSNs play a great role in the IoT ecosystem, with their provision of critical data to power intelligent decision-making and automation.
3. Control Systems and Automation: Orchestrating IoT Ecosystems
Control systems and automation technologies lend intelligence and decision-making capability to IoT devices and networks. The decisions these control systems make depend on the input that flows in from the sensors. This enables automation of processes, thereby transforming IoT ecosystems into self-regulating networks.
How Control Systems Drive IoT
Feedback Loops
A control system is based on feedback loops, where sensor data dictates changes in the performance of the system. For example, in an intelligent building, sensor data from temperature controls a control system to regulate the HVAC system and maintain the desired level of comfort.
Real-time decision-making
Advanced control systems, based on machine learning algorithms, allow IoT devices to make decisions in real-time. An example, to illustrate this best, is the autonomous vehicle. It needs control systems to process cameras and data coming in from LiDAR sensors while navigating safely.
Automation and IoT
Automation technologies enhance IoT through reduced human intervention. Smart factories employ robotic arms that are controlled by IoT systems in order to automate repetitive tasks, hence increasing efficiency and reducing errors.
Automation in IoT: Key Use Cases
Smart Agriculture: Automated irrigation systems adjust water flow based on soil moisture data.
Energy Management: Automated systems optimize energy consumption by turning off unused devices.
Transportation: Traffic management systems use IoT data to automate signal control and reduce congestion.
Control systems and automation technologies enable IoT ecosystems to function autonomously, making them more efficient and scalable.
Benefits of IoT Sensors Integration
The full potency of IoT lies in seamless integration into embedded systems and wireless sensor networks, control systems, and automation, intertwined together to form an ecosystem that can produce efficiency, intelligence, and innovation like never before.
1. Data Collection and Processing
Wireless sensor networks collect data from the environment while embedded systems process said data at the device level. This allows IoT devices to function independently yet still connect with central systems.
2. Intelligent Decision Making
The control systems use the information sensed to make intelligent decisions, and make real-time changes to system performance. This is further advanced by automation technologies, which execute the decisions made, without human interference.
3. Scalability and Flexibility
With all these technologies integrated, IoT ecosystems can scale easily in terms of accommodating new devices and functionalities. For example, incorporating new sensors in a smart city network is done without any trouble when embedded systems and WSNs are in place.
Conclusion
Embedded systems, wireless sensor networks, control systems, and automation are the building blocks that drive the IoT ecosystem. Each plays a distinguishable role, ranging from data collection to processing and from intelligent decision-making to automation.
By engaging these technologies, businesses and governments build smarter, more efficient systems regarding their mishaps across industries, including healthcare, agriculture, manufacturing, and transportation. What makes the IoT ecosystem of today so transformative is the synergy that these technology pieces create together.
As this science and technology continues to evolve, investing in these core technologies will be essential to stay ahead in the connected future. Whether you develop IoT solutions or adopt them, knowing the role of these technologies unlocks their full potential.