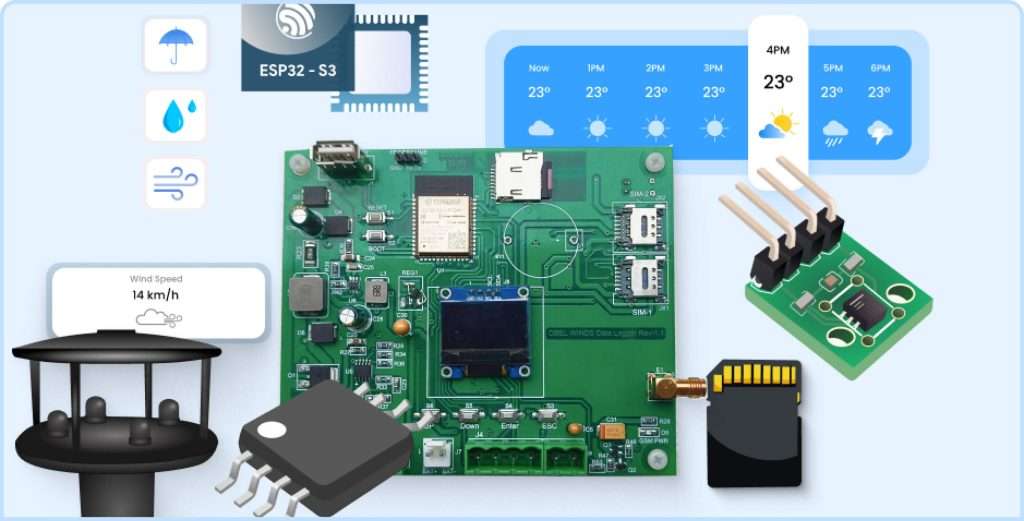
1. Integration of Multiple Sensor
IoT-based weather devices are built using multiple sensors to collect necessary parameters such as temperature, humidity, wind speed, and atmospheric pressure. Accordingly, because of this multi-sensor strategy, in-depth data gathering will be made about the weather to gain insights into the clear atmospheric conditions.
Use Case:
The smart company installs IoT weather stations across its fields with sensors that measure soil moisture levels, air temperature, and the strength of the wind speed. The data gathered may be communicated to help improve irrigation schedules or even shelter the crops from extreme weather conditions. For example, if the wind speed gets too aggressive, it is easy to take measures beforehand by covering fragile plants with netting or possibly even irrigation systems that would prevent water wastage.
2. Data Visualization
These devices are connected to the IoT platforms where data gets visualized in real-time. Users can have access to detailed weather reports, trends, and forecasts anywhere, enhancing decision-making.
Use Case:
Data would be input into an IoT weather monitoring system within the city management scenario that would feed into a central dashboard, which should provide real-time visualizations of temperature, humidity, and air quality levels within the city. Where the occurrence of a heatwave can lead to ascertaining which areas are most affected, thus deploying cooling centers and distributing resources in vulnerable populations.
3. Connectivity and Scalability
With the availability of IoT weather devices that offer connection via satellite, cellular networks, or Wi-Fi, they are assured to function correctly even in remote locations. They can also be scaled up for extra sensors to be integrated based on specific requirements.
Use Case:
A research organization focused on climate change builds an IoT network of remote weather stations. At the mid-point of the project, the needs arise to monitor other variables such as soil salinity and UV radiation. This feature of the IoT network enables them to integrate these sensors without a significant re-architecture into their existing facilities.
4. Solar-Powered Systems
Most of the IoT weather stations are now solar-powered and, hence, sustainable. However, this means that maintenance should not be constant or necessarily frequent, especially at a distance from the central station.
Use Case:
Nongovernmental organizations within the developing rural world have installed solar-powered weather stations to measure rainfall and temperature. Such stations provide real-time data to agricultural communities, enabling them to make informed decisions regarding planting and harvesting.
The utilization of solar-powered technology provides non-profit organizations with reduced operational costs and ensures continuous data acquisition in areas where minimum electricity is accessible for efficient agricultural practices.
5. Toughness and Weather Resistance
The devices are always made robust enough to endure different environmental conditions and, more often than not, waterproof and resistant to extreme temperatures, so it usually works in any weather.
Use Case:
An environmental research group tasked with assessing coastal erosion uses the rugged IoT weather stations, designed to withstand saltwater corrosion and the buffeting of winds. These send continuous data with regards to sea level and wave heights to facilitate integral data to be used for proper coastal management strategies. Upon the occurrence of storms, sensors remain steadfast, thus continuing to collect data uninterrupted, allowing researchers to accurately grade the effectivity of storms on coastal ecosystems.
6. Automated Alerts
The sensors of IoT weather devices can provide automatic alarms for extreme conditions and raise such critical alerts in serious cases of weather management and public safety.
Use Case:
Cities in flood-prone areas have installed IoT weather stations with flood detection sensors. The system automatically triggers an alert to the emergency services and to the persons around the area via SMS and social media. This quick response capacity allows the communities to evacuate or take the protective measures before flooding strikes, thereby seriously minimizing damage or loss of life.
Conclusion
With the inclusion of IoT technology within the weather monitoring device, this has introduced a new dimension of collecting and using atmospheric data. All of the important features involved such as multiple sensor integration, real-time data visualization, connectivity and scalability, solar-powered systems, durability, and automated alerts all enhance the decision-making ability in various industries.
There are such industries as agriculture and urban planning and disaster management that would be able to make informed decisions based on quite accurate real-time environmental data using these developed features. For instance, an individual might be able to optimize crop management practices, a municipality able to improve the resilience of a city towards climate events, or a researcher able to upgrade their studies about climate patterns.
IoT applies in monitoring weather to enhance operational efficiency while also contributing to safety and sustainability hence forming the central part of a modern approach to environmental management. Weather monitoring will continue to evolve through the advances in sensor technology bringing even more innovative applications and improvements thus predisposing to better preparation and response to environmental challenges.