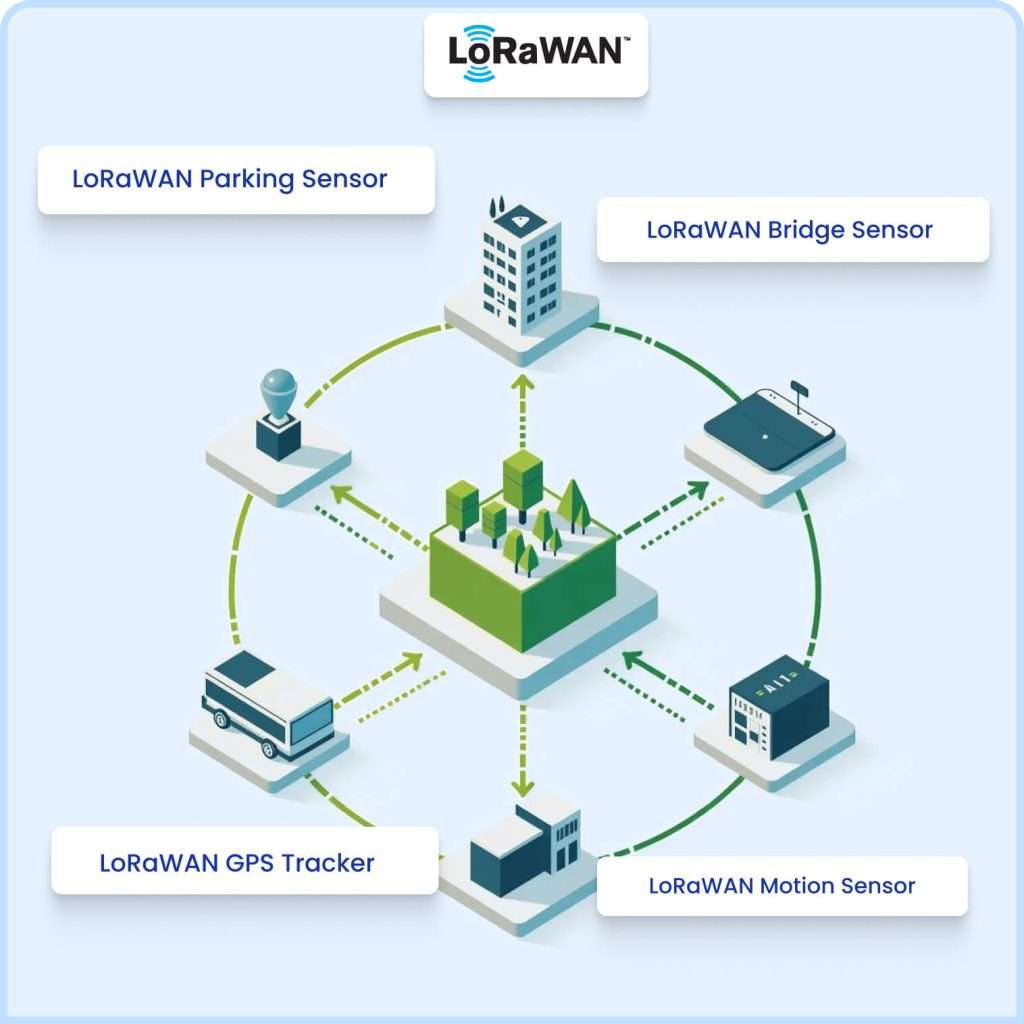
What's LoRaWAN?
LoRaWAN stands for low power wide area network, and it is a protocol that has been specifically designed for long range communications and involves minimal consumption of energy. These applications of the Internet of Things pertains to sending small data or information distance, through which the devices concerned send over the device with minimum energy consumption. LoRaWAN exploits unlicensed radio frequency bands making it possible for a wide range of applications.
LoRaWAN among some of the main features.
- It covers distances of up to 15 kilometers in rural areas and 2-5 kilometers in urban environments.
- Low Power Consumption: Devices can work for years on small batteries; hence, it is a cost-efficient way for deployment.
- Scalability: Millions of devices can be supported.
- Security: It comprises end-to-end encryption for upholding the integrity and privacy of data.
Role of LoRaWAN in Agriculture
1. Precision Farming
Precision farming incorporates information from different sources for decision making. The LoRaWAN sensors could be applied in measuring the level of soil moisture, temperature, humidity, and nutrient. Such data will enable one to have real-time scanning across the farm to ensure that irrigation and fertilization are optimized.
Use Case Example:
A vineyard uses LoRaWAN-enabled soil moisture sensors to maintain levels of water. It automatically sends messages to farmers on the exact time of irrigation to reduce waste of water while improving yields. This therefore offers chances to realize full potential in growth conditions by conserving resources.
2. Livestock Monitoring
The use of LoRaWAN will enable real-time monitoring of the health and location of livestock. Movement, health metrics, and behavioral attributes about how animals are faring will be monitored by sensors attached to animals.
It will require a GPS-enabled collar for tracking the movement of these cows and subsequently their health status. Information fetched is transmitted to a control room via LoRaWAN, and from there, the rancher can keep an eye on the herd’s health condition and any other concern which may crop up. This reduces the risk of disease breakout and hence overall herd management. Use LoRaWAN sensors to monitor environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and light intensity that impact crop health, enabling a farmer to detect crop diseases sooner and optimize growing conditions.
Example Use Case:
A farm that has a massive agricultural farmland monitors crop health real-time with LoRaWAN technology. The system takes in weather conditions, soil quality, and plant health and makes any data-driven decision made by the farmer about pest control or irrigation. In doing so, the crops are healthier and have more yield.
3. Supply Chain Optimization
The use of LoRaWAN can benefit the agricultural supply chain, as one can have real-time data about the condition of the goods in transit. It enables keeping products in the best conditions for transportation, which results in less waste and safer food.
Example Use Case:
One farm is employing LoRaWAN sensors to track the temperature and humidity of perishable products in transit. Alerts are triggered to the logistics team when temperatures fall outside the ideal range. Action taken promptly may mean that spoilage doesn’t occur. This not only helps prevent food spoilage but also boosts customer satisfaction.
LoRaWAN and Smart Cities
1. Smart Waste Management
In smart cities, LoRaWAN technology transforms waste collection route optimization and planning as well as schedules. Sensors placed in waste bins can monitor fill levels to enable the proper planning of efficient pickups for waste management companies.
Example Use Case
A smart waste management system for a city can be delivered through the LoRaWAN sensors placed inside public bins, collecting bin fill-level data for transmission to the central system to optimize the routes for collection routes that would thus avoid fuel wastages and costs.
2. Smart Lighting
LoRaWAN can deliver smart street lighting systems with adaptive adjustment to ambient light levels and pedestrian presence, not just enhancing safety but also cutting energy consumption.
Using Case:
A smart city installs LoRaWAN-enabled streetlights. When the hour is low, they dim but brighten in case pedestrians are detected. It helps to save energy and make sure streets are well-lit, enabling safe living, with reduced running costs.
3. Air Quality Monitoring
LoRaWAN can be deployed by cities for tracking air quality using sensors. A real-time data collection is done regarding the level of pollution and circulated to the people to make them aware of how much pollution there is, and accordingly policy decisions are made.
Using Case:
A city uses LoRaWAN sensors to monitor the air quality in several neighborhoods. The accessed data is presented as a mobile application to the citizens, who in return take the necessary precautions on days of poor air quality. This is, therefore, public health awareness and engrosses the people into activities.
4. Smart parking solutions
LoRaWAN can support smart parking systems that can guide drivers to available parking spots in real time. In this way, it would reduce congestion and emissions in urban areas.
Example Use Case:
A smart city installs LoRaWAN sensors to detect the availability of parking space in the city. These details are transmitted to a mobile app, through which drivers can find parking even more quickly. This helps reduce traffic and, in general, improves driving experience.
LoRaWAN and Smart Cities
1. Increased Efficiency
By introducing LoRaWAN to provide automation in data collection and analysis, more efficient resource management for agriculture and even for the urban region can be done. This is an aspect that conserves cost and saves resources aptly.
2. Enhanced Sustainability
LoRaWAN promotes sustainability by optimizing resource usage, reducing waste, and minimizing the negative impacts of agricultural and urban activities on the environment. In this regard, LoRaWAN is accompanied by the progressive efforts of the global world in sustaining sustainable practices.
3. Enhanced Productivity
In agriculture, real-time data enables the farmer to make better decisions that result in higher yields and better-quality products. In smart cities, improvements made in the infrastructure and services ensure that the city environment improves the quality of life for residents.
4. Scalability
Scalability to support an increased number of devices is inherent in LoRaWAN networks. This can be a requirement of cities with rapid expansion or farms with increased areas under cultivation. This flexibility makes it very suitable for both sectors.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Although LoRaWAN presents many opportunities, interoperability with other legacy systems is a challenge, alongside investment in the infrastructure and data privacy concerns. Because technology is produced and standards are continually being developed, these challenges can be overcome, and it will open the gates to a greater adoption.
Future Prospects
It promises a bright future for LoRaWAN in agriculture and smart cities. Indeed, with full assimilation of IoT-based solutions by more organizations, there will grow a stronger potential to be interconnected and to make decisions through data. Innovations in sensor technology, data analytics, and artificial intelligence will further enhance LoRaWAN application effectiveness.
Conclusion
LoRaWAN is changing agriculture and smart cities, as a robust framework for IoT connectivity is offered by LoRaWAN. With its support of long-range communications and low-power consumption capabilities, LoRaWAN has been proven to give wide-ranging benefits in precision farming, livestock monitoring, smart waste management, and much more. As the technology matures, it could mean even more sustainable, efficient, and connected communities.
With LoRaWAN, we may revolutionize the way we think about agriculture and urban settings; this is really an enhancement of the overall quality of life and continues toward the building of a more sustainable future. It provides a path for farmers who wish to increase productivity or planners working on designing a smarter urban environment in finding their way forward through LoRaWAN.