Part 5: Setting Up the Environment (Windows & macOS)
Before we start writing Appium tests, we need to set up our computer with the right tools and configurations. Don’t worry — We’ll guide you through every step.

Share at:
Prerequisites You’ll Need:
- Java JDK (latest version)
- Android Studio + Android SDK tools
- Node.js + npm (Node Package Manager)
- Appium Server
- Appium Inspector (optional but recommended)
- Device or Emulator setup
- Environment variables configuration


Step 1: Install Java JDK
Java is the programming language we’ll use, so we need to install its development kit.
- Go to Oracle’s Java Download page
- Download and install the latest JDK version (choose your OS version)
- After installation, verify in Command Prompt (Windows) or Terminal (macOS):
java -version
javac -version
You should see the installed version displayed.

Step 2: Install Android Studio and SDK Tools
Android Studio lets you run Android emulators and manage Android SDK.
- Download from: https://developer.android.com/studio
- Install and open Android Studio
- Use the SDK Manager (Tools > SDK Manager) to download:
- SDK Platforms (select the Android versions you want to test)
- SDK Tools (including platform-tools)
Step 3: Install Node.js and npm
Appium is built on Node.js, so install it next.
- Download from: https://nodejs.org
- Choose the LTS (Long-Term Support) version for stability
- Install it
- Verify installation by running in terminal/command prompt:
node -v
npm -v

Step 4: Install Appium Server
You can install Appium in two ways:
Option 1: Using npm (command line)
Open Terminal or Command Prompt and run:
npm install -g appium
This installs Appium globally.
To check if it’s installed correctly:
appium -v
Option 2: Appium Desktop (GUI)
If you prefer a graphical interface to start and inspect tests:
- Download from Appium Desktop Releases
- Install like any regular application


Step 5: (Optional) Install Appium Inspector
Appium Inspector lets you see your app’s UI elements, which helps write test scripts.
- It comes bundled with Appium Desktop, so if you installed that, you already have it.
- You can launch it from Appium Desktop


Step 6: Configure Android Device or Emulator
You need a target device to run tests on:
Emulator (Virtual Device):
- Open Android Studio
- Go to AVD Manager (Tools > AVD Manager)
- Create a new virtual device with the desired Android version
- Start the emulator
Real Android Device:
- Enable Developer Options and USB Debugging on your phone
- Connect your phone via USB
- Verify connection by running:
adb devices
- This should list your device.

Step 7: Set Environment Variables
You need to tell your computer where Java, Android SDK, and Node.js are installed.
On Windows:
- Open System Properties > Advanced > Environment Variables
- Add or edit these variables:
Variable
Value Example (adjust to your paths)
JAVA_HOME
C:\Program Files\Java\jdk-<version>
ANDROID_HOME
C:\Users\<YourUser>\AppData\Local\Android\Sdk
PATH
Add %JAVA_HOME%\bin;
%ANDROID_HOME%\platform-tools;
%ANDROID_HOME%\tools
On macOS/Linux:
Open Terminal and add these lines to your ~/.bash_profile or ~/.zshrc:
JAVA_HOME=$(/usr/libexec/java_home)
ANDROID_HOME=~/Library/Android/sdk
PATH=$PATH:$JAVA_HOME/bin:$ANDROID_HOME/platform-tools:$ANDROID_HOME/tools
Then run:
source ~/.bash_profile
(or source ~/.zshrc if you use zsh)
Step 8: Verify Everything Works
- Open a terminal or command prompt
- Run:
- Open a terminal or command prompt
- Run:
java -version
node -v
npm -v
appium -v
adb devices
If all return valid versions or your device list, you are good to go
Building complex IoT systems?
Accelerate testing and deployment with our QEMU-integrated toolchain expertise.
Mastering Appium: A Complete Beginner-to-Expert Mobile Automation Guide

Part 1 : Introduction to Mobile Automation and Appium
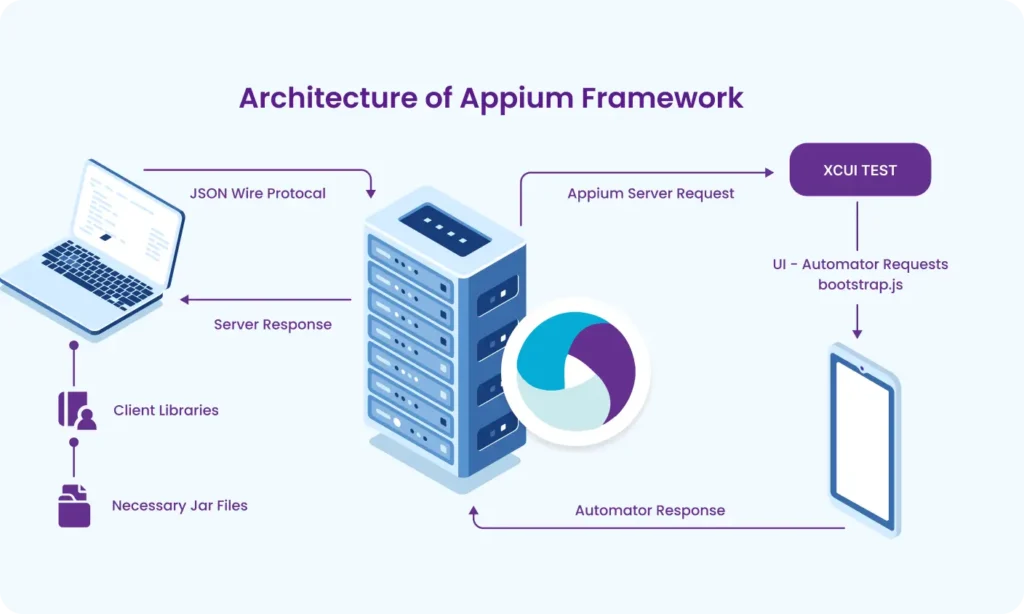
Part 2 : Appium Architecture, Tools Setup & How Test Code Connects to Devices
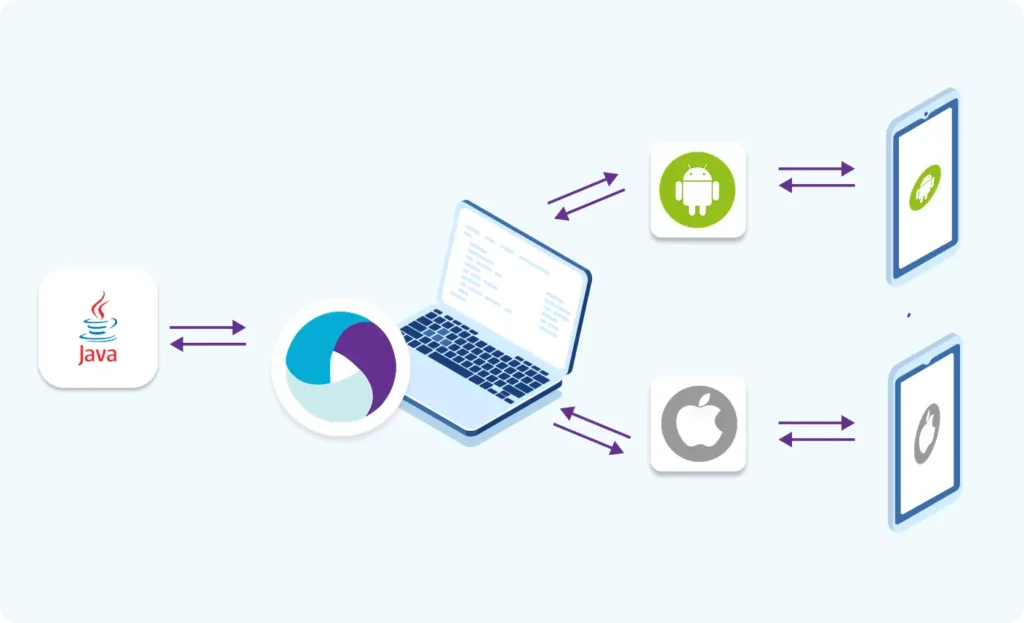
Part 3 : Java Fundamentals for Test Automation

Part 4 : Next Steps: Level Up Before Real Appium Scripting

Part 5 : Setting Up the Environment (Windows & macOS)

Part 6 : Understanding UiAutomator2 (Android Engine)
Part 7 : First Appium Test Script (Android)

Part 8 : Handling Waits and Synchronization in Appium (Android)
Part 9 : Element Locator Strategies in Android (ID, XPath, etc.)
Part 10 : TestNG Integration for Test Execution

Part 10.1 : Advanced TestNG Features in Appium Framework

Part 11 : Page Object Model (POM) Design in Appium (Android)

Part 12 : Logging with Log4j & Reporting with Extent Reports (Appium - Android)
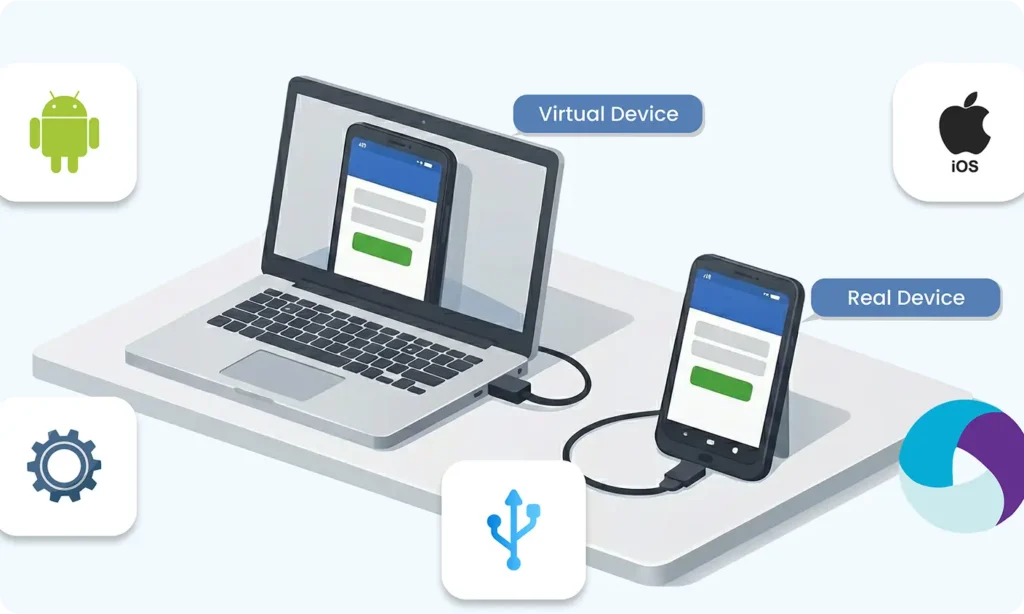

Part 13 : Real Devices vs Virtual Devices
