Part 8: Handling Waits and Synchronization in Appium (Android)


Share at:
Why Waits Are Important
In real mobile apps, elements don’t always appear immediately. For example:
- A login button may appear only after loading animation finishes.
- A popup may take a few seconds to show.
- The next screen might take time to load after clicking something.
If you try to interact with elements before they’re ready, Appium will throw errors like:
NoSuchElementException
ElementNotVisibleException
To prevent this, we use waits — which tell Appium:
Wait for the element to appear before doing anything.
Types of Waits in Appium
Appium (and Selenium) provide different wait strategies:
1. Implicit Wait (Set once for all elements)
Tells Appium to wait up to a certain time before throwing an error if an element is not found.
driver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
Example: If you write:
driver.findElement(By.id("some_id")).click();
Appium will try for up to 10 seconds to find that element before failing.
2. Explicit Wait (Target specific elements)
Used when you want to wait for a specific condition on a specific element.
WebDriverWait wait = new WebDriverWait(driver, 10);
WebElement element = wait.until(ExpectedConditions.visibilityOfElementLocated(By.id("some_id")));
This is more precise and powerful than implicit wait.
3. Fluent Wait (Advanced control)
Lets you set:
- How often to check for the element
- What exceptions to ignore
- Timeout duration
Used in complex apps, but not needed for beginners usually.
Example: Using Explicit Wait in Appium (Java)
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebElement;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.ui.ExpectedConditions;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.ui.WebDriverWait;
// Set explicit wait (10 seconds)
WebDriverWait wait = new WebDriverWait(driver, 10);
// Wait for a login button to become visible, then click
WebElement loginBtn = wait.until(ExpectedConditions.visibilityOfElementLocated(
By.id("com.example:id/btnLogin")));
loginBtn.click();
This will prevent the test from failing if the button takes a few seconds to appear.
Wait Best Practices
Do
Avoid
Use explicit waits for dynamic content
Relying only on Thread.sleep()
Combine with good locators
Using long waits for every element
Start with implicit + explicit waits
Mixing both blindly (they can conflict)
Bonus: Using Thread.sleep() (not recommended)
Thread.sleep(3000); // Wait for 3 seconds
Use only for:
- Debugging
- Testing wait behavior
This blocks everything and slows down tests.
Summary Table
Type of Wait
Use Case
Implicit Wait
Set once, wait for all elements by default
Explicit Wait
Wait for a specific condition on a specific element
Fluent Wait
Custom control (polling frequency, exceptions)
Thread.sleep()
Hard wait (not smart), use for debugging only
Building complex IoT systems?
Accelerate testing and deployment with our QEMU-integrated toolchain expertise.
Mastering Appium: A Complete Beginner-to-Expert Mobile Automation Guide

Part 1 : Introduction to Mobile Automation and Appium
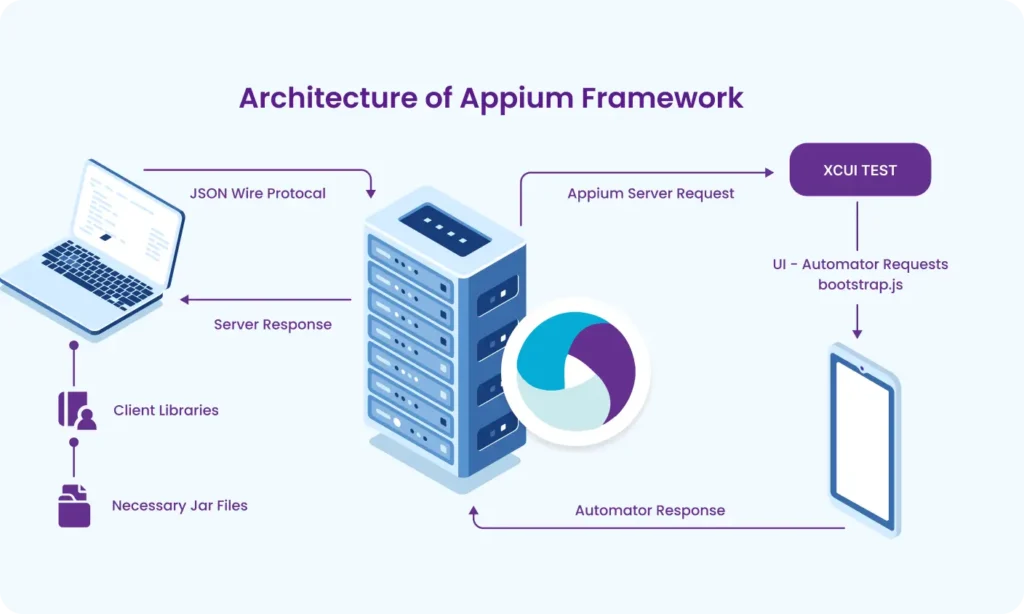
Part 2 : Appium Architecture, Tools Setup & How Test Code Connects to Devices
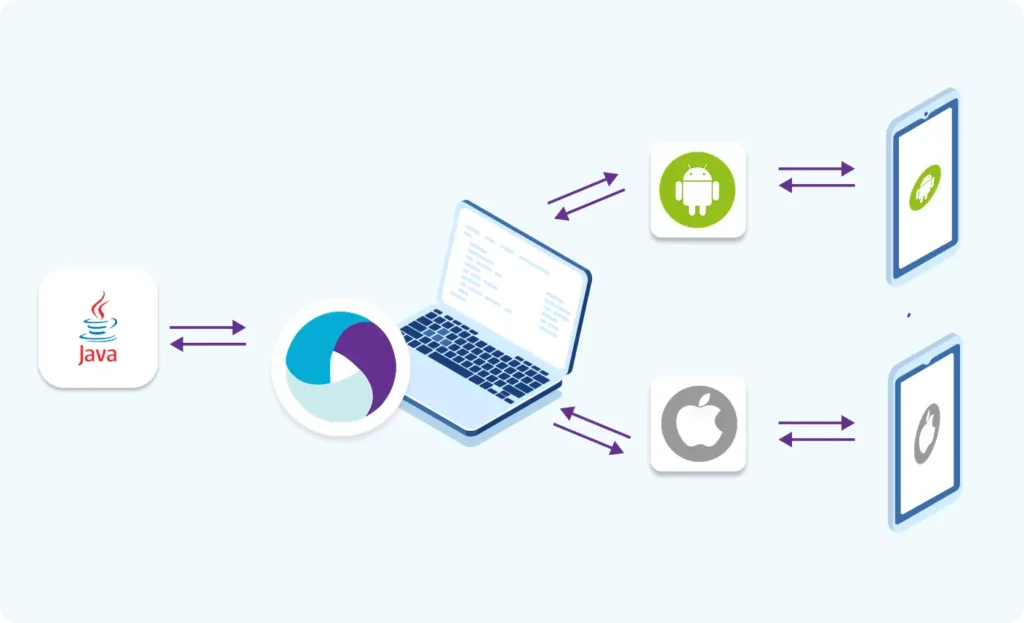
Part 3 : Java Fundamentals for Test Automation

Part 4 : Next Steps: Level Up Before Real Appium Scripting

Part 5 : Setting Up the Environment (Windows & macOS)

Part 6 : Understanding UiAutomator2 (Android Engine)
Part 7 : First Appium Test Script (Android)

Part 8 : Handling Waits and Synchronization in Appium (Android)
Part 9 : Element Locator Strategies in Android (ID, XPath, etc.)
Part 10 : TestNG Integration for Test Execution

Part 10.1 : Advanced TestNG Features in Appium Framework

Part 11 : Page Object Model (POM) Design in Appium (Android)

Part 12 : Logging with Log4j & Reporting with Extent Reports (Appium - Android)

Part 13 : Real Devices vs Virtual Devices
