Wi-Fi 6 & Wi-Fi 7 — The Next Leap in Wireless Connectivity
What is it?
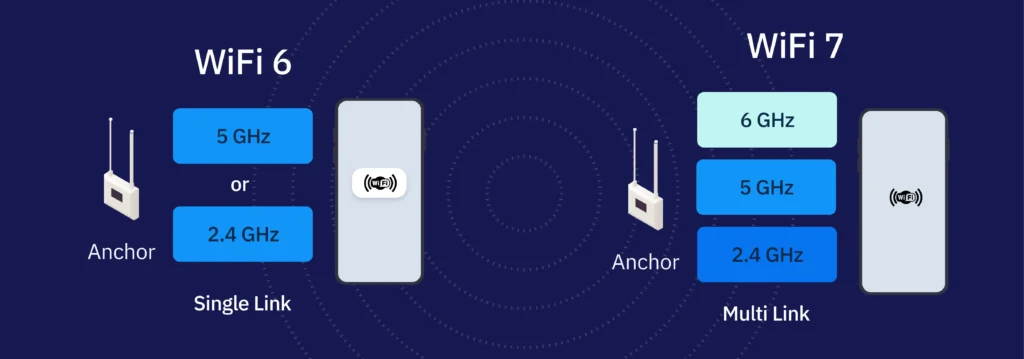
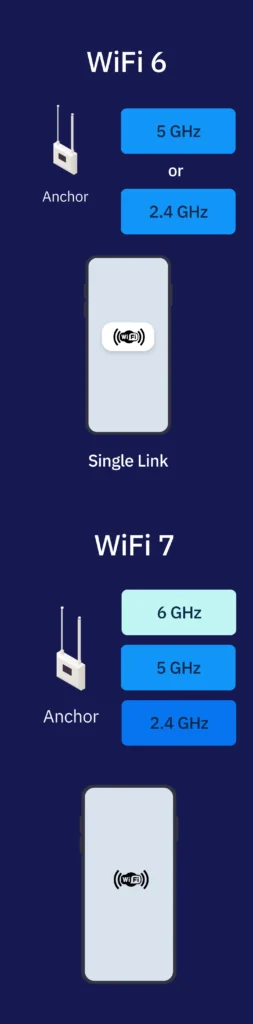
Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) and Wi-Fi 7 (802.11be) represent the latest generations of wireless networking standards designed to meet the explosive demand for high-speed, low-latency, and reliable connectivity. While Wi-Fi 6 focused on efficiency and multi-device performance, Wi-Fi 7 takes it further by unlocking ultra-high throughput, real-time responsiveness, and deterministic networking for Industry 4.0 applications.
Share at:
Evolution of Wi-Fi Standards
Wi-Fi technology has continuously evolved to meet the ever-growing demand for speed, connectivity, and reliability.
- Wi-Fi 4 (802.11n, 2009): Introduced MIMO and speeds up to 600 Mbps.
- Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac, 2013): Boosted speeds to ~3.5 Gbps and improved streaming performance.
- Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax, 2019): Focused on efficiency, multi-device performance, IoT battery life, and dense deployments.
- Wi-Fi 6E (2020): Extended Wi-Fi 6 into the 6 GHz spectrum for reduced interference.
- Wi-Fi 7 (802.11be, 2024+): Breakthrough with up to 46 Gbps, sub-1 ms latency, Multi-Link Operation, and deterministic networking for real-time orchestration.
Each generation has been built on the previous one — Wi-Fi 6 brought efficiency, while Wi-Fi 7 now delivers real-time responsiveness and scalability for Industry 4.0.
Features
Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax):
- Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) for efficient spectrum usage.
- MU-MIMO (multi-user, multiple-input, multiple-output) for better multi-device handling.
- Target Wake Time (TWT) for improved IoT battery life.
- Peak data rates ~9.6 Gbps.
Wi-Fi 7 (802.11be):
- Extremely High Throughput (EHT) with speeds up to 46 Gbps.
- Multi-Link Operation (MLO) to bond multiple channels for reliability.
- 320 MHz channel bandwidth support.
- Preamble Puncturing for flexible spectrum usage.
- Latency below 1 ms — enabling AR/VR, robotics, and real-time IoT orchestration.
Wi-Fi 6 vs Wi-Fi 7: Key Differences
Feature
Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax)
Wi-Fi 7 (802.11be)
Peak Speed
Up to ~9.6 Gbps
Up to ~46 Gbps
Channel Bandwidth
20 / 40 / 80 / 160 MHz
20 / 40 / 80 / 160 / 320 MHz
Latency
~10 ms
<1 ms (ultra-low latency)
MU-MIMO
Uplink & Downlink (up to 8 streams)
Expanded MU-MIMO (up to 16 streams)
OFDMA
Yes
Enhanced with more flexible scheduling
Multi-Link Operation
Not supported
Supported — simultaneous multi-band use
Preamble Puncturing
Limited flexibility in channel use
More advanced spectrum utilization
Device Density
Supports thousands of devices per AP
Optimized for very high-density IoT networks
Security
WPA3 standard
WPA3 + improved network slicing & encryption
Best Fit Use Cases
IoT, healthcare, smart homes, enterprise Wi-Fi
AR/VR, robotics, industrial IoT, orchestration, defence
Use Cases
- Smart Manufacturing: Ultra-reliable wireless links for automated machinery and real-time monitoring.
- Hospitals: High-speed, interference-free connectivity for patient monitoring devices.
- Logistics & Warehousing: Seamless real-time asset tracking with uninterrupted network coverage.
- Smart Cities: High-density sensor networks for surveillance, traffic management, and IoT.
- Defence & Training: VR/AR-enabled immersive training and situational awareness.
Technologies + Existing Products
- Chipsets: Qualcomm Networking Pro Series, Intel Wi-Fi 6E/7 cards, MediaTek Filogic.
- Routers & Access Points: TP-Link Archer BE900, Netgear Nighthawk RS700, Cisco Meraki Wi-Fi 6 APs.
- IoT Devices: Smart wearables, connected healthcare devices, and industrial IoT gateways with Wi-Fi 6 modules.
Advantages
- Massive Device Density: Handle thousands of IoT sensors in a single network.
- Ultra-Low Latency: Mission-critical operations like autonomous vehicles and telemedicine.
- Energy Efficiency: Extends battery life of IoT endpoints with TWT.
- Deterministic Networking: Predictable performance, critical for Industry 4.0 and orchestration platforms like SyTrak.
- High Bandwidth: Smooth AR/VR, cloud gaming, and 8K streaming.
Limitations
- Infrastructure Upgrade Costs: Wi-Fi 6/7 routers, gateways, and chipsets are expensive, especially for large-scale deployments.
- Backward Compatibility Issues: While standards support older devices, performance gains are limited unless the entire ecosystem upgrades.
- Spectrum Availability: Wi-Fi 7’s full potential relies on the 6 GHz band, which isn’t universally available worldwide.
- Power Demands: Higher throughput can increase energy consumption on access points and gateways.
- Interference in Dense Environments: Despite improvements, overlapping signals in very high-density setups may still affect performance.
Security Enhancements in Wi-Fi 6 & 7
Security is central to enterprise and IoT adoption. Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 7 bring improvements that make them enterprise-ready:
- WPA3 Security Protocol: Stronger encryption and password protection against brute-force attacks.
- Enhanced Data Privacy: Individualized data encryption between each device and the access point.
- Improved IoT Security: Target Wake Time (TWT) in Wi-Fi 6 minimizes device exposure windows, reducing attack vectors.
- Network Slicing (Wi-Fi 7): Ability to allocate dedicated, secure channels for specific applications (e.g., healthcare monitoring, defence communication).
- Deterministic Networking: Wi-Fi 7 ensures predictable, secure packet delivery for mission-critical tasks.
These upgrades make Wi-Fi 6 and 7 not only faster but also safer for industrial IoT, healthcare, and defence applications.
Transforming Operations with Wi-Fi 6 & 7 in Krishworks Technology Innovations & SyTrak
At Krishworks Technology Innovations, Wi-Fi 6 & 7 technologies play a critical role in building resilient, scalable, and efficient orchestration platforms for Industry 4.0.
SyTrak (Industrial Orchestration)
- Real-Time Tracking: Wi-Fi 7’s low latency and Multi-Link Operation enable continuous monitoring of personnel, assets, and vehicles with near-zero downtime.
- Dense Deployments: Wi-Fi 6 ensures reliable connectivity for thousands of IoT devices across warehouses, factories, and hospitals.
Embedded IoT Devices
Wi-Fi 6 modules in weather stations, vending machines, and smart locks improve connectivity reliability while extending battery life with TWT.
Fleet Management
Wi-Fi 7-powered edge gateways allow faster synchronization of OBD2 and CAN bus data, improving fleet health insights in real time.
Defence Projects
Support immersive AR/VR training and real-time situational awareness through Wi-Fi 7’s ultra-low latency and multi-gigabit throughput.
Healthcare Monitoring
Wi-Fi 6 enables uninterrupted health parameter tracking in smart handcuffs, wearable monitors, and patient devices while keeping power consumption low.
In summary:
Wi-Fi 6 laid the foundation for efficient, high-density IoT networks/ multi-device handling, while Wi-Fi 7 takes connectivity to the next level with ultra-high speeds, sub-millisecond latency, and deterministic networking. Together, they help industries to scale into true Industry 4.0 environments.
At Krishworks Technology Innovations, we see these standards as enablers for real-time orchestration, smart automation, and next-gen asset visibility. Through SyTrak and our IoT solutions, Wi-Fi 6 and 7 are not just faster connections — they are the backbone of safer, smarter, and more efficient industrial operations.