Part 12 : Logging with Log4j & Reporting with Extent Reports (Appium – Android)


In this part of the series, we move into two important components of any professional automation framework : logging and reporting.
Writing test scripts is only one part of automation. You must also be able to :
- Understand what happened during the test run
- Identify where and why a test failed
- Share clear results with your team
Logging and reporting help you achieve this.
- Log4j is used for printing test execution logs
- ExtentReports is used to generate visual HTML reports
Share at:
1. Why Do We Need Logging and Reporting?
A reliable automation framework should provide clarity about the test execution flow. Logging and reporting allow you to :
- Track each action the script performs
- Quickly debug failures
- Find the root cause of issues
- Share readable reports with QA engineers, developers, and managers
Without logging and reporting, troubleshooting becomes difficult, especially in large test suites.
2. Logging with Log4j
What is Log4j?
Log4j is a Java-based logging library. It allows you to add custom messages throughout your code, such as :
- “App launched”
- “Login button clicked”
- “Element not found”
These messages help you trace the execution flow and understand what happened at each step.

Step 1 : Add Log4j dependency in pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.17</version>
</dependency>
Step 2 : Create log4j.properties
Create this file under :
src/test/resources/log4j.properties
Add the following configuration :
log4j.rootLogger=INFO, file, stdout
# Print to console
log4j.appender.stdout=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.stdout.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.stdout.layout.ConversionPattern=%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss} %-5p %c{1}:%L - %m%n
# Print to file
log4j.appender.file=org.apache.log4j.FileAppender
log4j.appender.file.File=logs/test-log.log
log4j.appender.file.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.file.layout.ConversionPattern=%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss} %-5p %c{1}:%L - %m%n
Step 3 : Use Log4j in your test
import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
public class LoginTest {
Logger log = Logger.getLogger(LoginTest.class);
public void loginTest() {
log.info("Launching App");
log.debug("Debug: entering credentials");
log.error("Element not found");
}
}
3. Reporting with ExtentReports
Why ExtentReports?
ExtentReports is a popular reporting tool for automation frameworks because it produces:
- Clean and professional HTML reports
- Logs for each test step
- Pass and fail status
- Screenshot support
These reports are easy to understand and can be shared with anyone.
Step 1 : Add ExtentReports dependency
<dependency>
<groupId>com.aventstack</groupId>
<artifactId>extentreports</artifactId>
<version>5.0.9</version>
</dependency>
Step 2 : Basic ExtentReports setup
ExtentReports extent = new ExtentReports();
ExtentHtmlReporter htmlReporter = new ExtentHtmlReporter("reports/test-report.html");
extent.attachReporter(htmlReporter);
ExtentTest test = extent.createTest("Login Test");
test.pass("App launched");
test.fail("Login failed");
extent.flush(); // save the HTML report
4. Taking Screenshots on Failure
Screenshots are extremely helpful when a test fails because they show the exact state of the app at the moment of failure.
Capture the screenshot
File src = ((TakesScreenshot) driver).getScreenshotAs(OutputType.FILE);
FileUtils.copyFile(src, new File("screenshots/test-failure.png"));
Attach the screenshot in ExtentReports
test.fail("Test failed",
MediaEntityBuilder.createScreenCaptureFromPath("screenshots/test-failure.png").build());
5. Recommended Folder Structure
/logs - Log4j output
/reports - Extent HTML reports
/screenshots - Screenshots captured on failures
/src/test/java - Test classes and page objects
/src/test/resources - config files, log4j properties
Summary
In this part, you learned how to add logging and reporting to your Appium automation framework. These are essential features because they provide clarity, help with debugging, and allow teams to understand test results quickly.
Logging and reporting are foundational elements of a scalable framework and prepare you for more advanced topics in the coming sessions.
Building complex IoT systems?
Accelerate testing and deployment with our QEMU-integrated toolchain expertise.
Mastering Appium: A Complete Beginner-to-Expert Mobile Automation Guide

Part 1 : Introduction to Mobile Automation and Appium
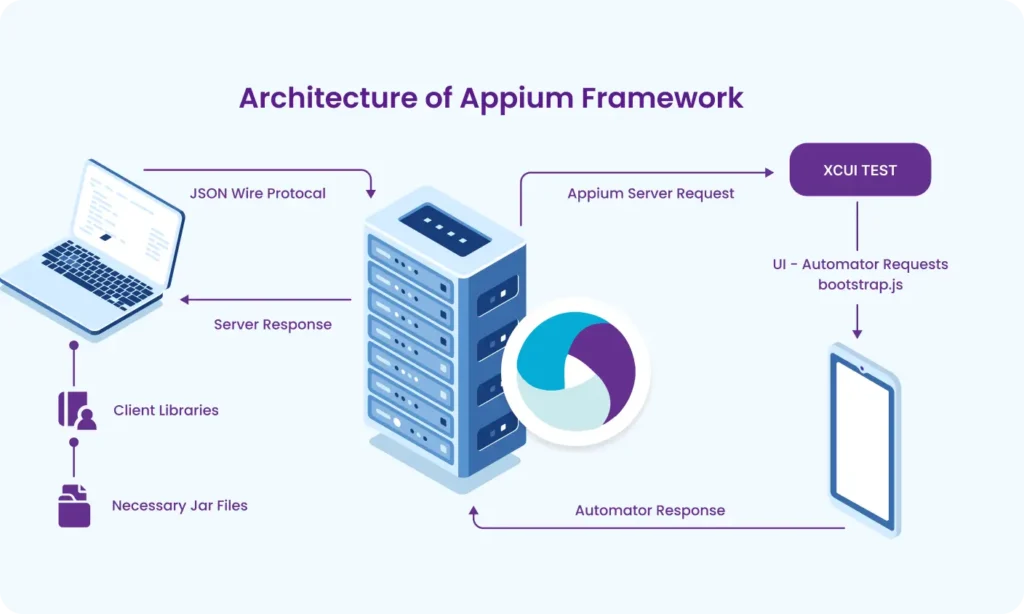
Part 2 : Appium Architecture, Tools Setup & How Test Code Connects to Devices
Part 3 : Java Fundamentals for Test Automation

Part 4 : Next Steps: Level Up Before Real Appium Scripting

Part 5 : Setting Up the Environment (Windows & macOS)

Part 6 : Understanding UiAutomator2 (Android Engine)
Part 7 : First Appium Test Script (Android)

Part 8 : Handling Waits and Synchronization in Appium (Android)
Part 9 : Element Locator Strategies in Android (ID, XPath, etc.)
Part 10 : TestNG Integration for Test Execution

Part 10.1 : Advanced TestNG Features in Appium Framework

Part 11 : Page Object Model (POM) Design in Appium (Android)

Part 12 : Logging with Log4j & Reporting with Extent Reports (Appium - Android)

Part 13 : Real Devices vs Virtual Devices
