Appium Mobile Automation Tutorial – From Scratch to Expert Level
Welcome to this hands-on Appium tutorial series
If you’re new to mobile automation or want to take your skills to the next level, you’re in the right place. In this series, we’ll start from the basics and work our way up to building a complete, real-world Appium framework.
Appium is an open-source tool used for automating mobile apps on Android and iOS. It supports testing of native, hybrid, and mobile web apps, and works with languages like Java, Python, and JavaScript.

Table of Contents
- Part 1 : Introduction to Mobile Automation and Appium
Part 2 : Appium Architecture, Tools Setup & How Test Code Connects to Devices
- Part 3 : Java Fundamentals for Test Automation
- Part 4 : Next Steps: Level Up Before Real Appium Scripting
- Part 5 : Setting Up the Environment (Windows & macOS)
- Part 6 : Understanding UiAutomator2 (Android Engine)
- Part 7 : First Appium Test Script (Android)
- Part 8 : Handling Waits and Synchronization in Appium (Android)
- Part 9 : Element Locator Strategies in Android (ID, XPath, etc.)
- Part 10 : TestNG Integration for Test Execution
- Part 10.1 : Advanced TestNG Features in Appium Framework
- Part 11 : Page Object Model (POM) Design in Appium (Android)
- Part 12 : Logging with Log4j & Reporting with Extent Reports (Appium – Android)
- Part 13 : Real Devices vs Virtual Devices
- Part 14 : iOS Automation Basics (XCUITest)
Share at:
What This Tutorial Covers
This is a complete, hands-on Appium tutorial series designed to take you from absolute beginner to expert, starting from the basics and gradually building a full-scale mobile automation framework.
Key Topics You’ll Learn:
- Setting up Appium from scratch (Android & iOS)
- Understanding Appium Architecture and Desired Capabilities
- Writing test scripts using TestNG
- Building frameworks using Maven and Page Object Model (POM)
- Adding logging with Log4j and test reporting with Extent Reports
- Integrating with Jenkins for CI/CD pipelines
- Running tests on real devices, emulators, and cloud platforms
Parallel test execution across devices for faster feedback
By the End of This Series, You'll Be Able To:
Automate mobile apps on both Android and iOS platforms
Build robust, scalable, maintainable automation frameworks
Integrate your tests with modern tools used in real-world projects
Run your tests efficiently in local and cloud environments
Who Is This For?
- Beginners who want to get started with mobile automation
- Manual testers moving into automation
- Automation engineers looking to expand into mobile testing
- Anyone who wants to build a professional-grade Appium framework from scratch
By the end of this tutorial, you’ll have a complete automation framework ready for real-world use — and you’ll be comfortable testing apps across platforms and environments.
Let’s get started
Connect. Monitor. Control. — accelerate your IoT product development with our end-to-end expertise
Appium Automation - Lecture Series Contents
A complete beginner-to-expert series to help you master mobile automation using Appium, Java, and the latest tools in the industry.
Part 1: Introduction to Mobile Automation and Appium
- What is mobile automation?
- Why automate mobile testing?
- Appium overview and key benefits

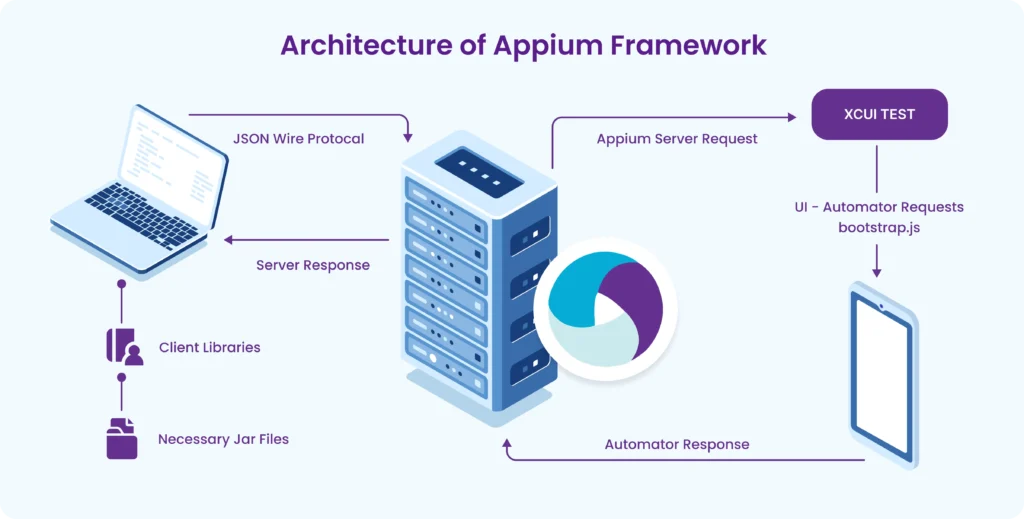
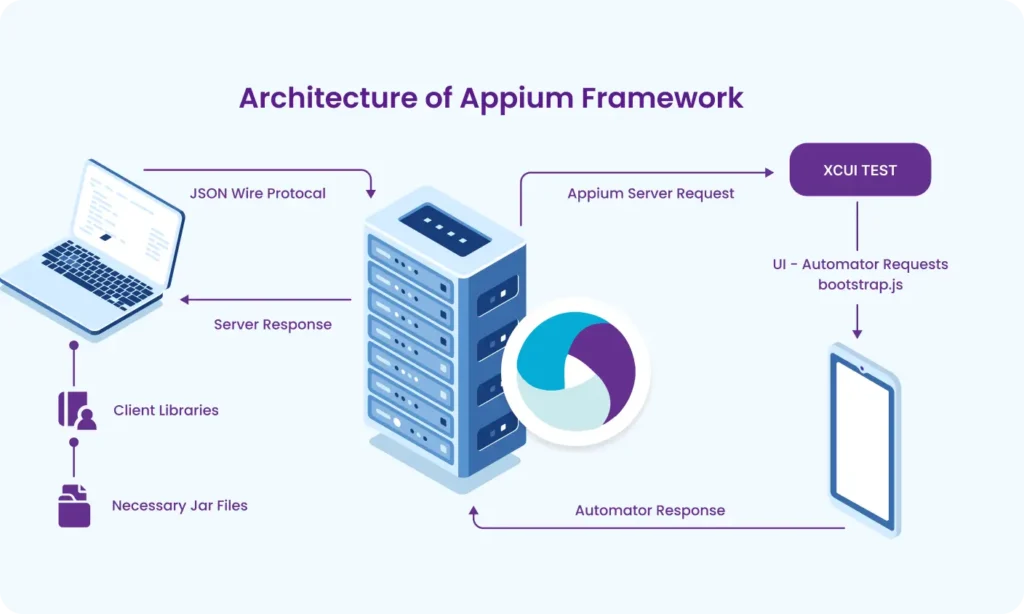
Part 2: Appium Architecture, Tools Setup & How Test Code Connects to Devices
- Appium client-server-driver architecture
- Tool installation (Java, Node.js, Android Studio, Appium, etc.)
- How Appium interacts with Android and iOS devices/emulators
Part 3: Java Fundamentals for Test Automation
- Core Java concepts required for Appium
- Classes, objects, methods, loops, collections
- Hands-on practice with Eclipse

Part 4 : Next Steps: Level Up Before Real Appium Scripting
- Practice Writing Methods, Loops, and Conditions
- Create a Utility Class and Call Methods from main()
Build Comfort Before Writing Real Appium Scripts- Summary of Next Steps

Part 5: Setting Up the Environment (Windows & macOS)
- Step-by-step setup on Windows
- Setting up Appium on macOS (including Xcode for iOS)
- Emulator & device configuration

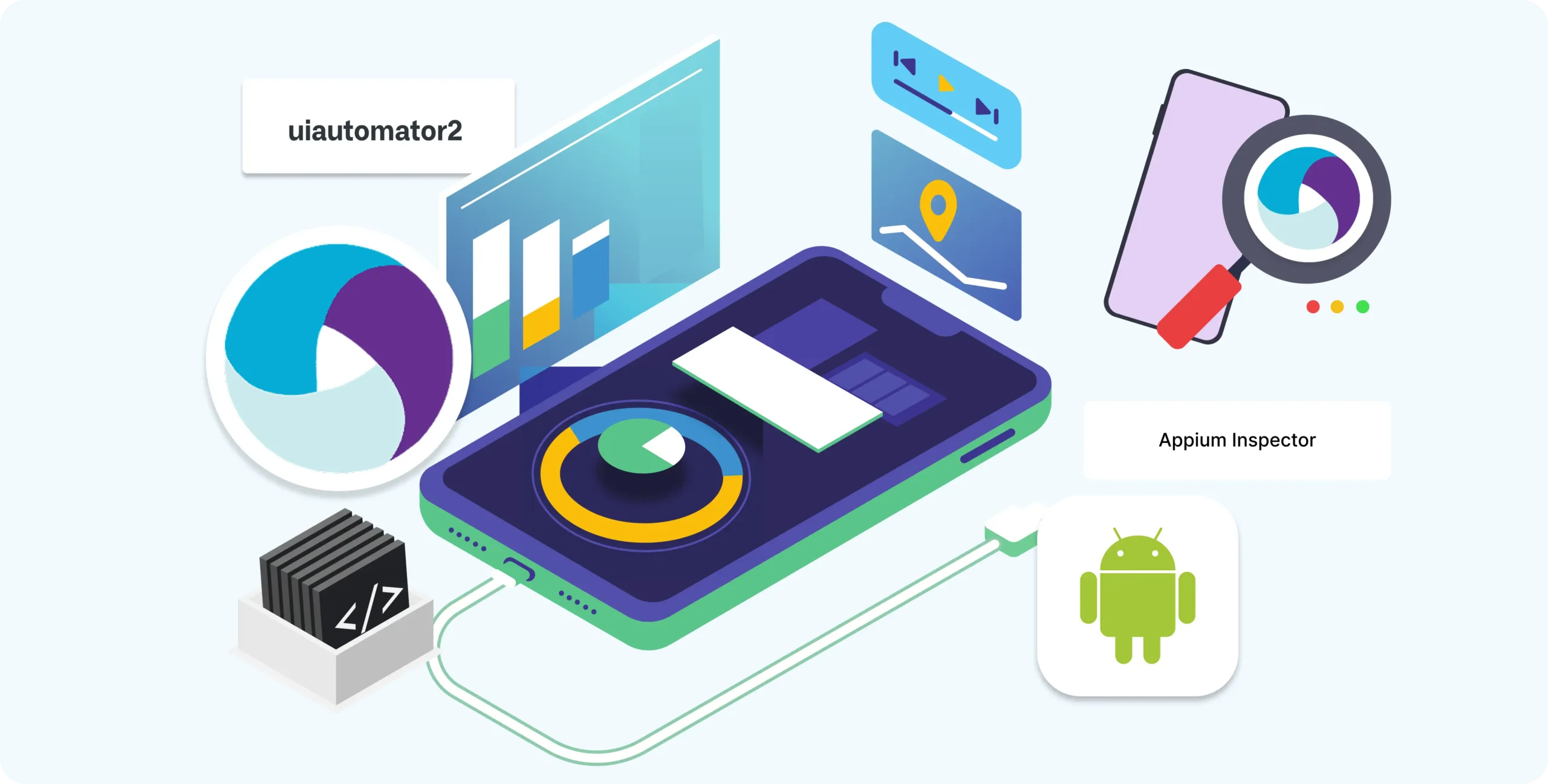
Part 6: Understanding UiAutomator2 (Android Engine)
- What is UiAutomator2?
- How Appium uses it to automate Android apps
- Differences between UiAutomator2 and older drivers like Selendroid

Part 7: First Appium Test Script (Android)
- Writing your first real test in Java with Appium
- Connecting to emulator/device
- Launching the app and performing basic actions (click, send keys, etc.)

Part 8: Handling Waits and Synchronization in Appium (Android)
- Understand why waits are essential in mobile automation.
- Learn how to handle delays when elements take time to appear.
- Explore different wait strategies: Implicit, Explicit, and Fluent Waits.Prevent errors like NoSuchElementException and ElementNotVisibleException.
- Learn best practices for synchronizing test execution.
- Understand why using Thread.sleep() is not recommended.
- Make your Appium tests more stable and reliable by waiting smartly for elements.

Part 9: Element Locator Strategies in Android (ID, XPath, etc.)
- Learn how to locate elements on a mobile screen for automation.
- Understand the purpose of locators: tell Appium which element to click, type into, or verify.
- Tools to find locators: Appium Inspector (live inspection) and UIAutomatorViewer (static snapshot).
- Common locator strategies:
- By ID (resource-id) – fast, reliable, recommended first choice.
- By Accessibility ID (content-desc) – good for buttons/icons and accessibility testing.
- By XPath – flexible but slower; use only if ID or accessibility ID isn’t available.
- By Class Name – for groups of elements, not always unique.
- Android UIAutomator – advanced targeting, scrolling, and filtering.
Part 10: TestNG Integration for Test Execution
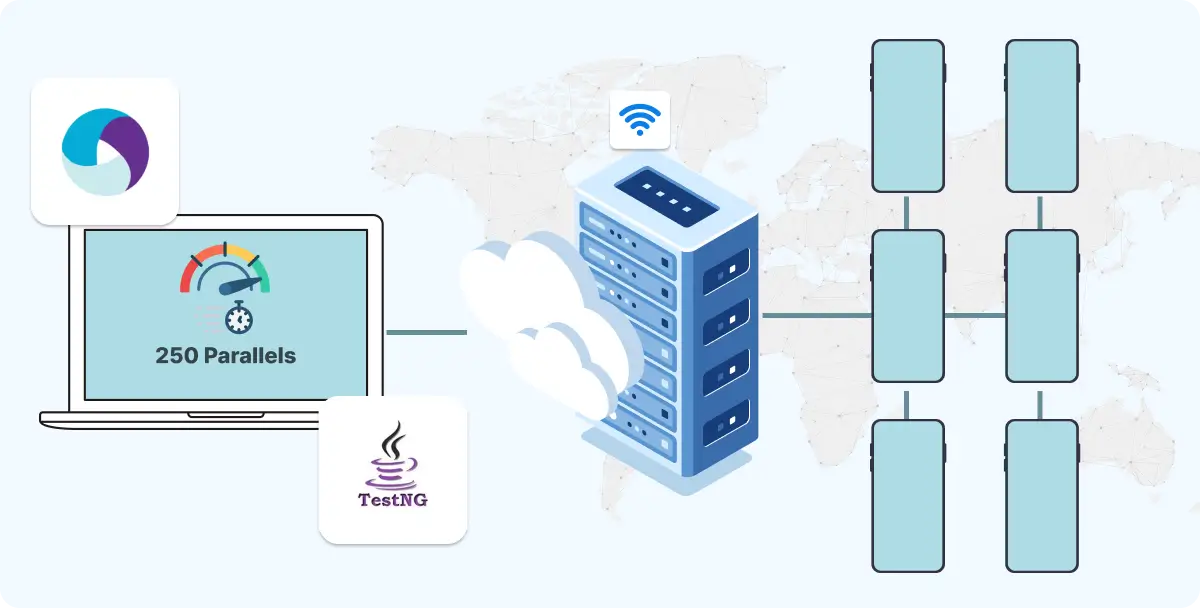
- TestNG helps manage Appium test execution, including setup, teardown, parallel runs, and reporting.
- Add TestNG dependency in Maven (pom.xml) to enable its features.
- Use annotations:
- @BeforeClass – initialize Appium driver
- @Test – test logic
- @AfterClass – close driver/session
- Use testng.xml to organize suites, classes, and parallel execution.
- Features for Appium projects:
- DataProvider – run tests with multiple inputs
- Parallel execution – run tests on multiple devices simultaneously
- Parameters – pass device-specific data like UDID or systemPort
- Advanced features:
- Listeners – take actions on test events (screenshots, logs)
- Retry Analyzer – automatically rerun flaky tests
- Custom reports – integrate with ExtentReports or Allure
- Easy CI/CD integration with Maven commands and Jenkins pipelines.
- Summary: TestNG organizes, scales, and enhances Appium test automation.
Part 10.1: Advanced TestNG Features in Appium Framework
- TestNG Listeners – Automate actions on test events (e.g., screenshots on failure, logging, custom reporting).
- Retry Analyzer – Automatically re-run flaky or unstable tests using
IRetryAnalyzer. - Custom Reporting – Integrate advanced reporting tools like ExtentReports or Allure for detailed visual reports.
- Parallel Execution – Run tests simultaneously on multiple devices/emulators using TestNG parameters.
- Parameterization – Pass device-specific capabilities (e.g., UDID, system port) via
testng.xml. - CI/CD Integration – Easily execute TestNG + Appium tests in Jenkins, GitHub Actions, or other pipelines.

Part 11: Page Object Model (POM) Design in Appium (Android)
Introduction to POM – Each app screen is represented as a class with its own elements and actions.
- Benefits of POM – Cleaner, reusable, and easily maintainable test code.
- Reusable Screen Classes – Create separate classes for each screen (e.g.,
LoginScreen) with element locators and actions. - Reduced Code Duplication – Reuse screen methods across multiple tests instead of rewriting element locators.
- Scalable Framework – POM helps organize large automation projects into modular components.
- Best Practices – One screen = one class, avoid test logic inside screen classes, use clear method names, and implement explicit waits.
- Project Structure – Organized folders for
base,screens,tests, andutilsto support scalability. - Base Test Setup – Common setup and teardown for initializing the Appium driver.
- Writing Tests Using POM – TestNG tests call methods from screen classes, keeping test logic clean.

Part 12 : Logging with Log4j & Reporting with Extent Reports (Appium – Android)
- Logging and reporting are essential for debugging and transparency.
- Log4j for execution logs, ExtentReports for professional reporting.
- Lays the foundation for scalable and maintainable automation frameworks.

Part 13 : Real Devices vs Virtual Devices
- Setting Up the Android Emulator (Virtual Device)
- Connecting a Real Android Phone Using USB
- Tips for Testing on Physical Devices
- Common Device Setup Errors (and Simple Fixes)

Part 14 : iOS Automation Basics (XCUITest)
This lesson provides a foundational understanding of iOS automation using XCUITest. It explains why iOS automation is limited to macOS and introduces the core tools required, including Xcode, Carthage, and WebDriverAgent. Learners will gain insight into how Appium leverages XCUITest for iOS automation, set up both simulators and real iPhones, and write their first automated iOS test case.

Mastering Appium: A Complete Beginner-to-Expert Mobile Automation Guide

Part 1 : Introduction to Mobile Automation and Appium
Part 2 : Appium Architecture, Tools Setup & How Test Code Connects to Devices
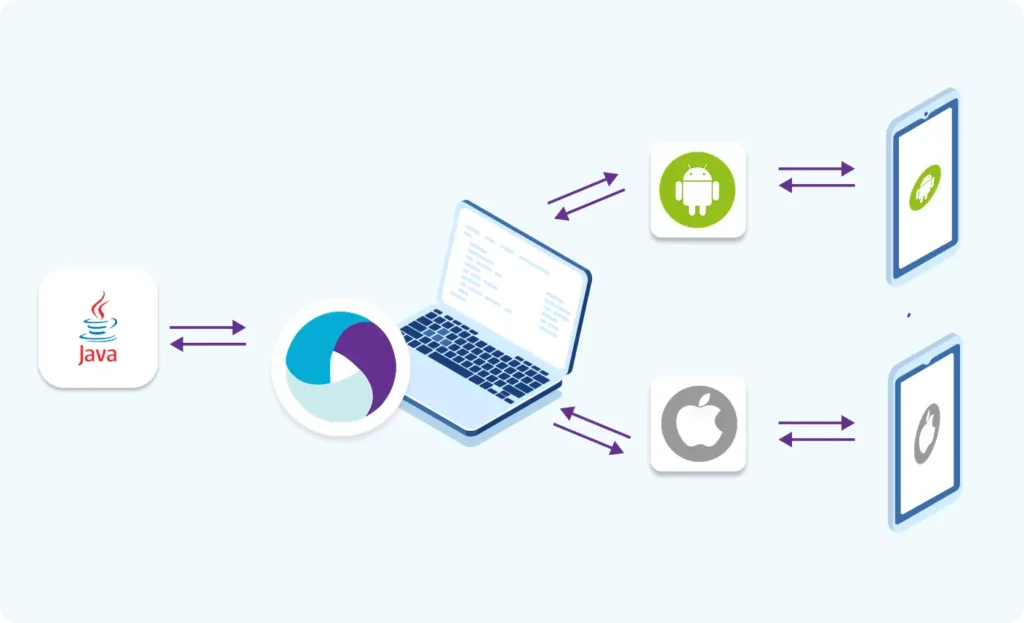
Part 3 : Java Fundamentals for Test Automation

Part 4 : Next Steps: Level Up Before Real Appium Scripting

Part 5 : Setting Up the Environment (Windows & macOS)

Part 6 : Understanding UiAutomator2 (Android Engine)
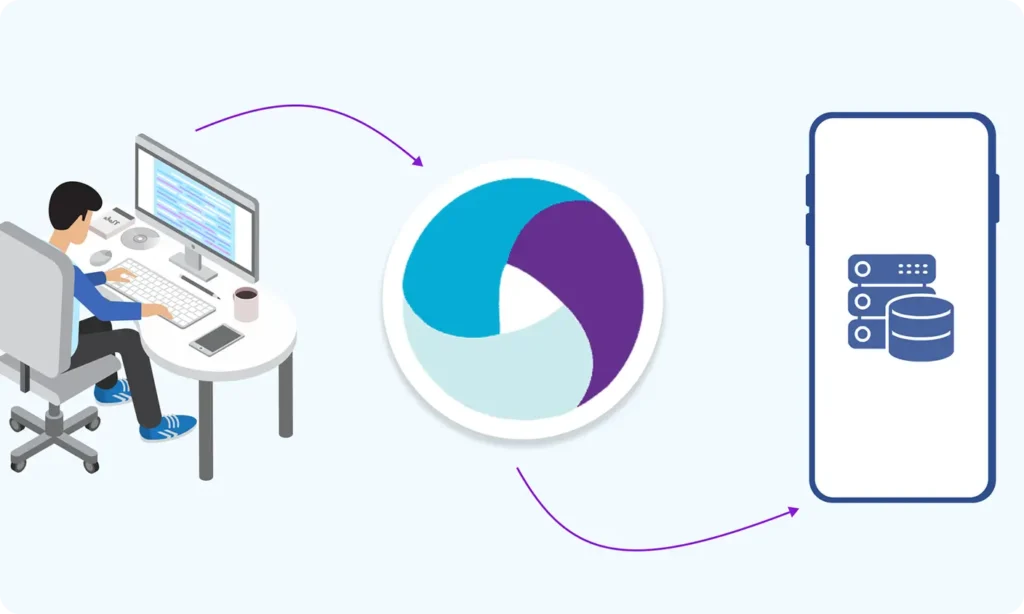
Part 7 : First Appium Test Script (Android)

Part 8 : Handling Waits and Synchronization in Appium (Android)
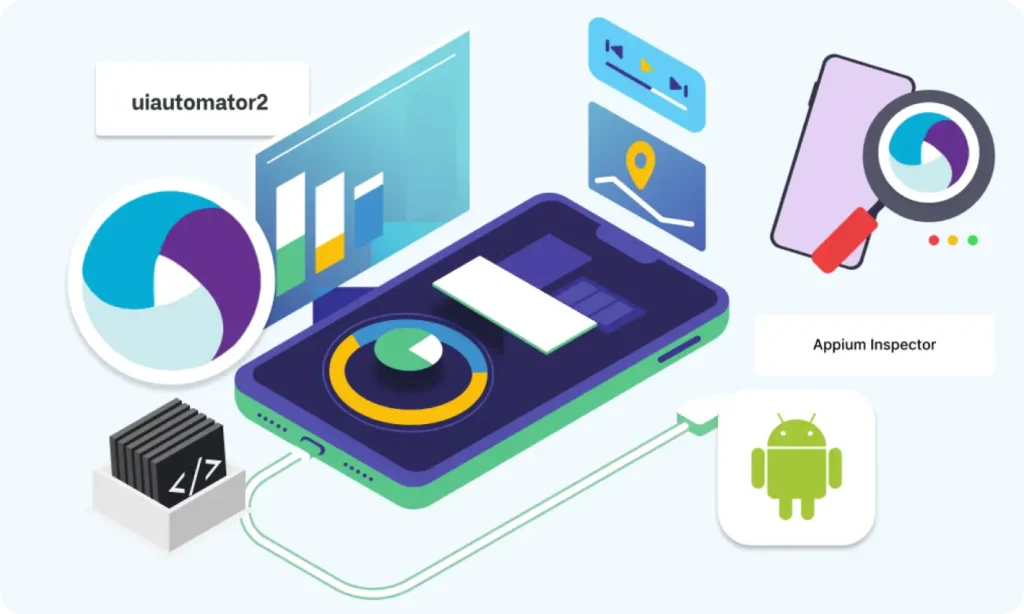
Part 9 : Element Locator Strategies in Android (ID, XPath, etc.)
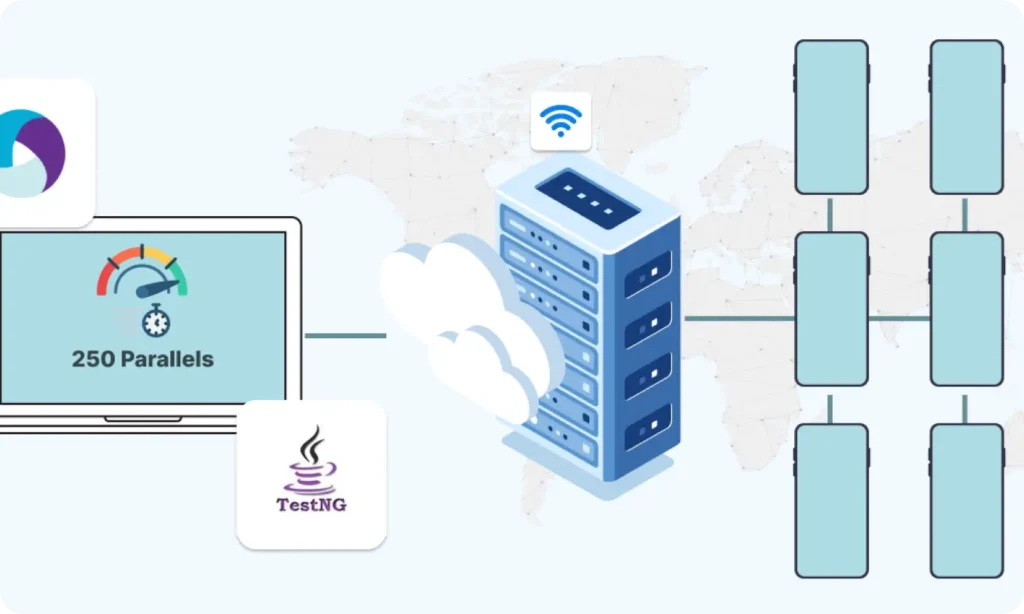
Part 10 : TestNG Integration for Test Execution

Part 10.1 : Advanced TestNG Features in Appium Framework

Part 11 : Page Object Model (POM) Design in Appium (Android)

Part 12 : Logging with Log4j & Reporting with Extent Reports (Appium - Android)

Part 13 : Real Devices vs Virtual Devices
