Part 14 : iOS Automation Basics (XCUITest)
- What is XCUITest?
- macOS-only requirements:
- Xcode
- Carthage
- WebDriverAgent
- Setting up simulator or real iPhone
- Writing first iOS test with Appium

Share at:
1. What is XCUITest?
XCUITest is Apple’s native UI testing framework for iOS apps.
It is built on top of XCTest and is used to automate:
- iOS apps
- iPadOS apps
- tvOS apps
Key Points
- Developed and maintained by Apple
- Written in Swift or Objective-C
- Direct access to iOS UI elements
- Faster and more stable than older tools (like UIAutomation)
Role in Appium
Appium uses XCUITest as the automation backend for iOS devices.
Appium → WebDriver protocol → WebDriverAgent → XCUITest → iOS App
2. MacOS-Only Requirements (Why macOS?)
iOS automation cannot be done on Windows or Linux because:
- Apple restricts iOS development tools to macOS
- Xcode is mandatory
3. Required Tools Explained
3.1 Xcode
Xcode is Apple’s official IDE.
Used for :
- iOS SDKs
- Simulators
- Compiling WebDriverAgent
- Signing apps
Required version depends on:
- iOS version
- Xcode version compatibility
3.2 Carthage
Carthage is a dependency manager for macOS.
Why Appium needs it:
- WebDriverAgent dependencies are managed via Carthage
Install :
brew install carthage

3.3 WebDriverAgent (WDA)
WebDriverAgent is the bridge between Appium and XCUITest.
Responsibilities:
- Launching the app
- Finding UI elements
- Performing taps, swipes, typing
- Sending responses back to Appium
Location :
node_modules/appium-webdriveragent/
Must be :
- Compiled
- Signed
- Installed on simulator or real device
3.4 Simulator or Real iPhone Setup
iOS Simulator
- Comes with Xcode
- No provisioning profile needed
- Faster setup
- Limited hardware feature testing
Real iPhone
- Requires Apple Developer account
- Provisioning profile & signing
- Needed for :
- Push notifications
- Camera
- Face ID / Touch IDt
- Real-world behavior
4. Architecture Overview
Test Script (Java / Python / JS)
↓
Appium Server
↓
WebDriverAgent (XCUITest)
↓
iOS App (Simulator / Device)
5. Writing Your First iOS Test with Appium (Example)
5.1 Start Appium Server
appium
5.2 Desired Capabilities (Example – Java)
IOSOptions options = new IOSOptions();
options.setPlatformName("iOS");
options.setPlatformVersion("17.0");
options.setDeviceName("iPhone 15");
options.setAutomationName("XCUITest");
// App path (.app for simulator, .ipa for real device)
options.setApp("/path/to/MyApp.app");
// Optional but useful
options.setNoReset(true);
options.setNewCommandTimeout(300);
5.3 Create Driver
IOSDriver driver = new IOSDriver(
new URL("http://localhost:4723/wd/hub"),
caps
);
5.4 First Test Action
driver.findElement(By.name("Login")).click();
5.5 Quit Session
driver.quit();
6. Common XCUITest Locator Strategies
- accessibility id (preferred)
- name
- label
- class chain
- predicate string
- xpath (last option)
Example :
driver.findElement(AppiumBy.accessibilityId("usernameField"));
7. Advantages of XCUITest with Appium
- Official Apple framework
- High stability
- Supports modern iOS versions
- Works on simulators and real devices
8. Common Challenges (Beginner Awareness)
- Code signing errors
- WebDriverAgent build failures
- Xcode version mismatch
- iOS updates breaking compatibility
Summary
- XCUITest is Apple’s native iOS automation framework
- Appium uses XCUITest via WebDriverAgent
- macOS + Xcode are mandatory
- Ideal for scalable, cross-platform mobile automation
Building complex IoT systems?
Accelerate testing and deployment with our QEMU-integrated toolchain expertise.
Mastering Appium: A Complete Beginner-to-Expert Mobile Automation Guide

Part 1 : Introduction to Mobile Automation and Appium
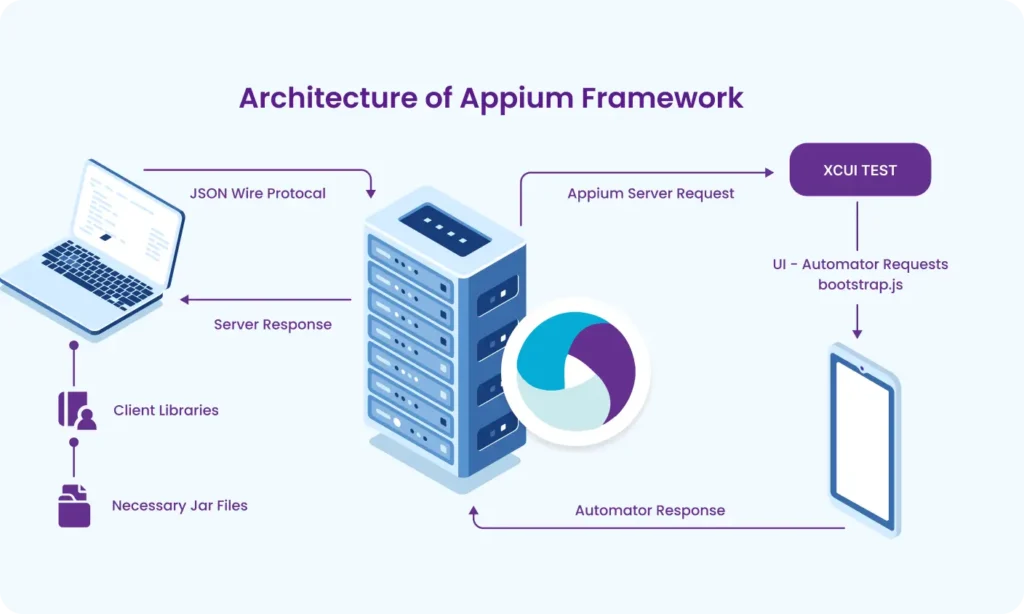
Part 2 : Appium Architecture, Tools Setup & How Test Code Connects to Devices
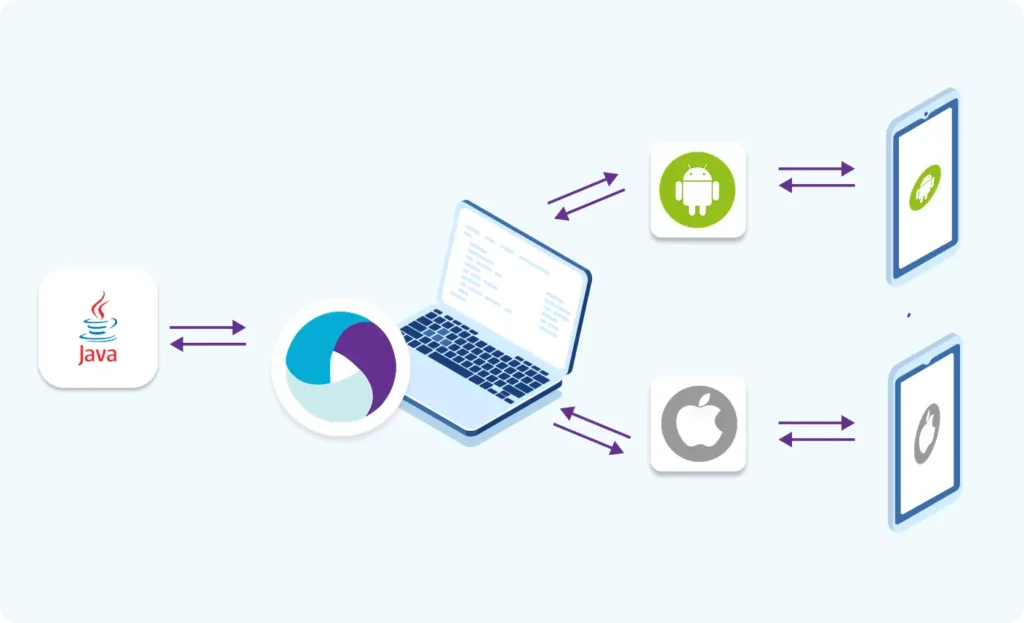
Part 3 : Java Fundamentals for Test Automation

Part 4 : Next Steps: Level Up Before Real Appium Scripting

Part 5 : Setting Up the Environment (Windows & macOS)

Part 6 : Understanding UiAutomator2 (Android Engine)
Part 7 : First Appium Test Script (Android)

Part 8 : Handling Waits and Synchronization in Appium (Android)
Part 9 : Element Locator Strategies in Android (ID, XPath, etc.)
Part 10 : TestNG Integration for Test Execution

Part 10.1 : Advanced TestNG Features in Appium Framework

Part 11 : Page Object Model (POM) Design in Appium (Android)

Part 12 : Logging with Log4j & Reporting with Extent Reports (Appium - Android)

Part 13 : Real Devices vs Virtual Devices
