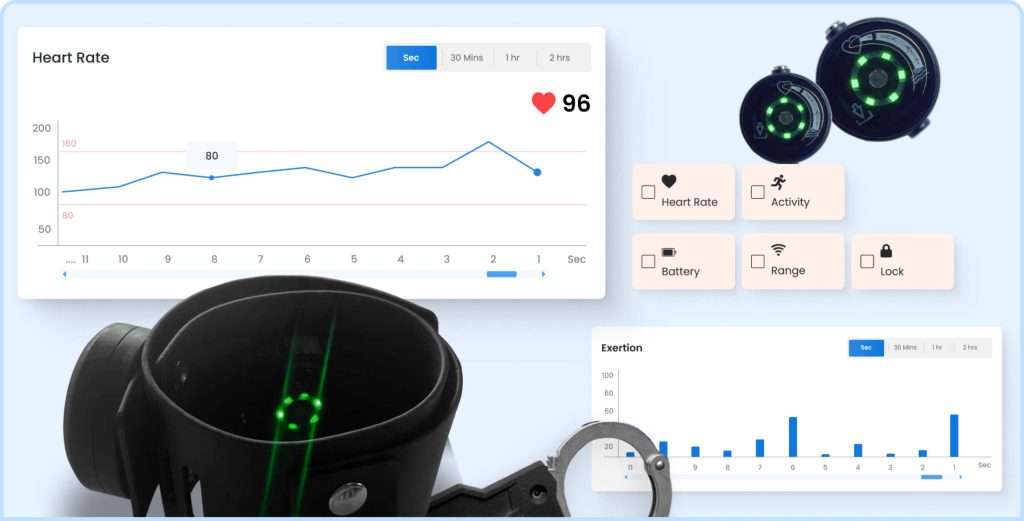
1. Continuous Monitoring
Continuous monitoring is an integral part of health monitoring IoT devices. These devices track vital signs, for instance, heart rate, blood pressure, blood glucose levels, and oxygen saturation in real time.
Advantages:
Early diagnosis: By continuous monitoring of vital signs, healthcare providers may be able to detect any abnormality early, which in turn means timely intervention. For instance, patients suffering from chronic diseases like diabetes tend to benefit immensely through the continuous real-time monitoring of blood glucose levels.
Increased Patient Engagement: Patients can also track their own health trends thus increasing consciousness and responsibility towards health.
2. Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)
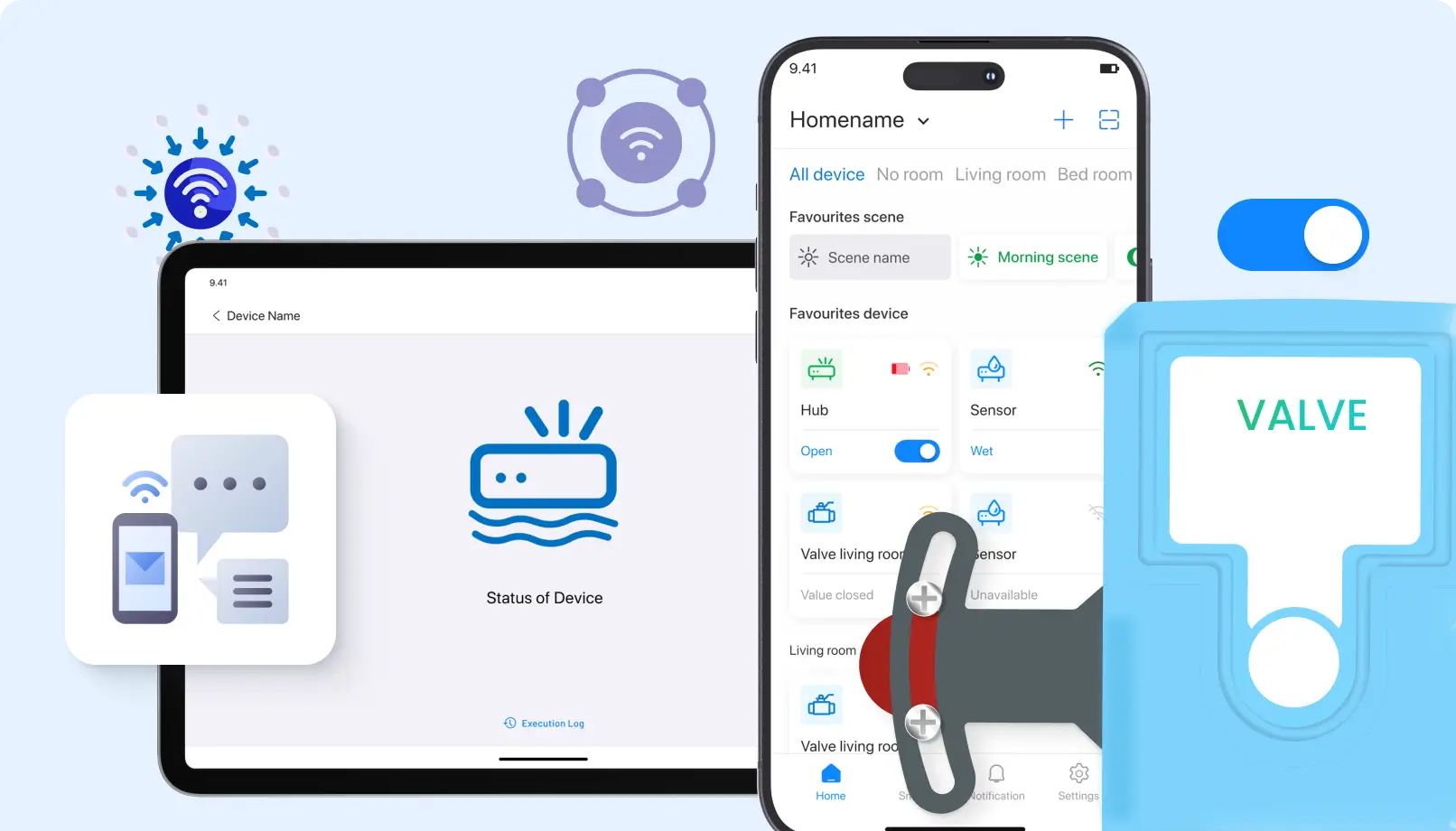
RPM is the observation of patients’ health data as monitored from their homes using health IoT devices. It is very helpful to patients with chronic conditions requiring monitoring without frequent visits to hospitals.
Advantages:
It is convenient: Many patients can receive care from their homes, benefiting those with some mobility difficulties.
Cost-Effective: RPM reduces the number of times a patient needs to visit the hospital, thus saving the patients and providers costs associated with healthcare.
3. Data Analytics and Visualization
Health monitoring IoT devices collect vast amounts of data that, if analyzed, might ascertain trends and patterns in patients’ health. These analyses can then be visualized across user-friendly dashboards accessible to healthcare providers.
Advantages:
More Informed Decisions: Information analytics avails the healthcare provider the chance to make decisions based on information they have to improve the patient’s results. For example, they may opt to change medications because they notice trends in a patient’s blood pressure.
Personalized Care: These treatments will be more accurate based on individual data gathered from the patients.
4. Electronic Health Records (EHR)
Heal Health monitoring IoT devices can be easily integrated with EHRs, so that the patient data are transferred automatically.
Benefits:
workflow: Integration is seen to avoid time-consuming and labor-intensive work of adding data individually, reduces errors, and saves health professionals’ time.
Global Health Picture: Since EHR integration is capable of making all the patient data, including the real-time monitoring data, appear at one place, this will give an all-around view of the health status of a patient.
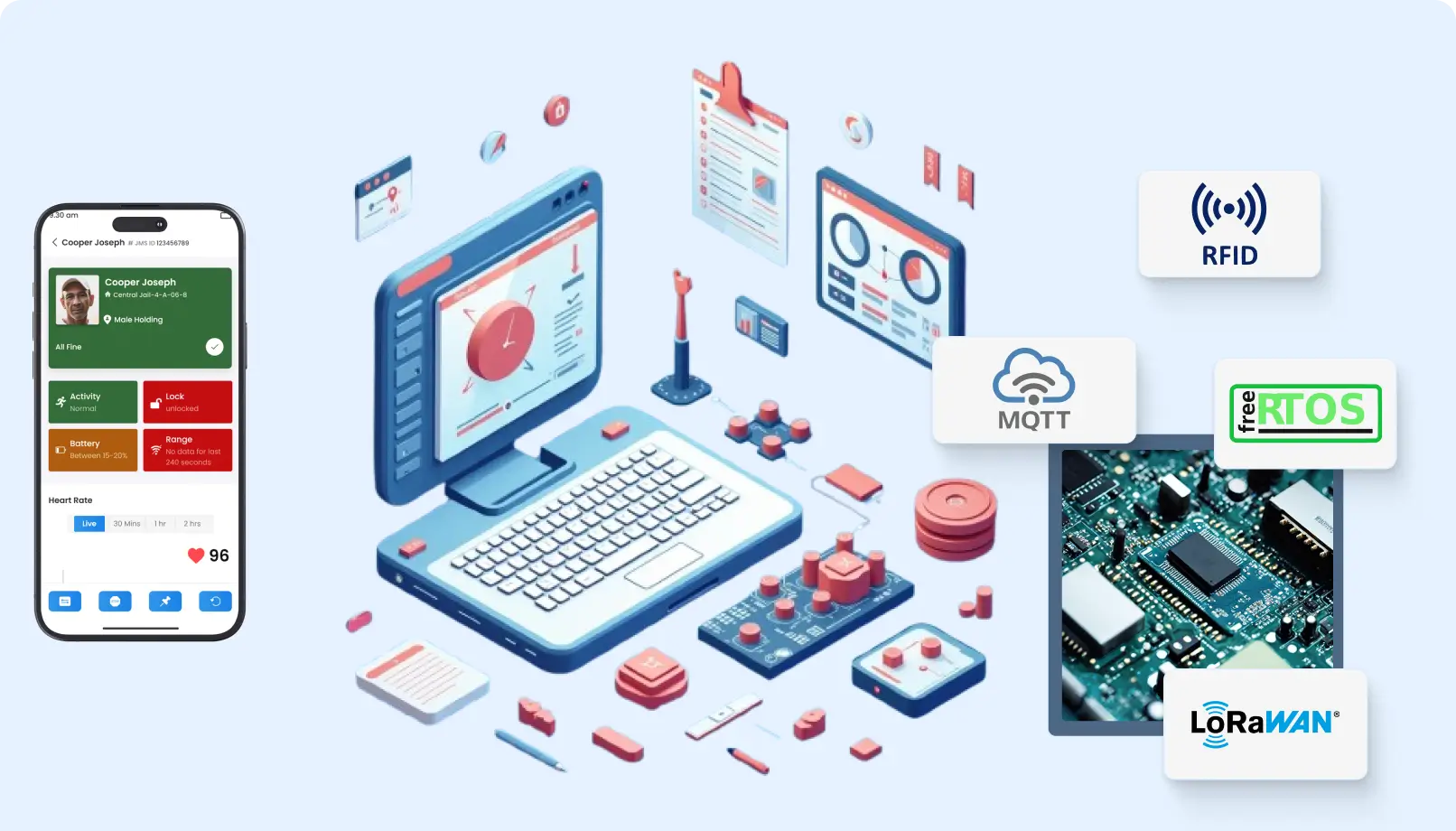
6. Features of Emergency Response
Health monitoring IoT devices can include emergency response features such as automatic alerting of healthcare providers and emergency contacts in the event of a critical health event.
Benefits:
Speedy Response: Automated alerts can diminish the time taken to respond to an emergency situation by several folds, which in many cases might even be a matter of life and death.
Relief among patients and their families: Patients and their families enjoy an added sense of relief, knowing that help is just a notification away.
7. Medication Management
IoT devices can be handy in managing medications through reminding patients when to take their drugs and tracking their adherence.
Benefits:
Improved Adherence: Reminders ensure that the patient does not forget his/ her medication schedule in time, thus reducing the complications related thereto.
Side Effects Monitoring: Following side effects reporting from the patient, the adherence to the medication by monitoring, treatment plans can be adjusted to suit individual needs.
8. Wearable Technology
Wearable health monitoring devices include smartwatches, fitness trackers, and any specialized medical devices that are developed to monitor ongoing health metrics.
Benefits:
Variety: Wearables can track many health metrics, such as levels of activity, heart rate, and sleep pattern, thereby giving a 360-degree view of a person’s health.
Real-time Feedback: Most wearables give real-time feedback on health metrics to encourage users to adopt healthier lifestyles.
9. Advanced Security and Privacy
With the rise of health monitoring IoT devices, the problem of security and privacy arises. Advanced encryption and authentication features ensure the safety of patient data.
Protection of Sensitive Data: Advanced features ensure access protection to patients’ sensitive health information.
Regulatory Compliance: Most IoT health devices are based on regulatory requirements in various countries, including HIPAA in the U.S., to ensure protection of patient confidentiality.
Conclusion
Health monitoring IoT devices are transforming the healthcare scene by delivering caring intelligence, and everything they offer-from continuous monitoring to remote patient monitoring-to data analytics, integration with EHRs, and user-friendly interfaces-empowers both patients and healthcare providers.
Indeed, as the technologies move further, it will be truly possible for the healthcare monitoring IoT devices to do even more. What this means is that their services would become even more personal and accessible while adding a little bit of efficiency towards the healthcare provision. As a matter of fact, this technology would greatly advance patient care and outcome, changing the whole future health care paradigm.