Understanding RFID Technology
What is RFID?
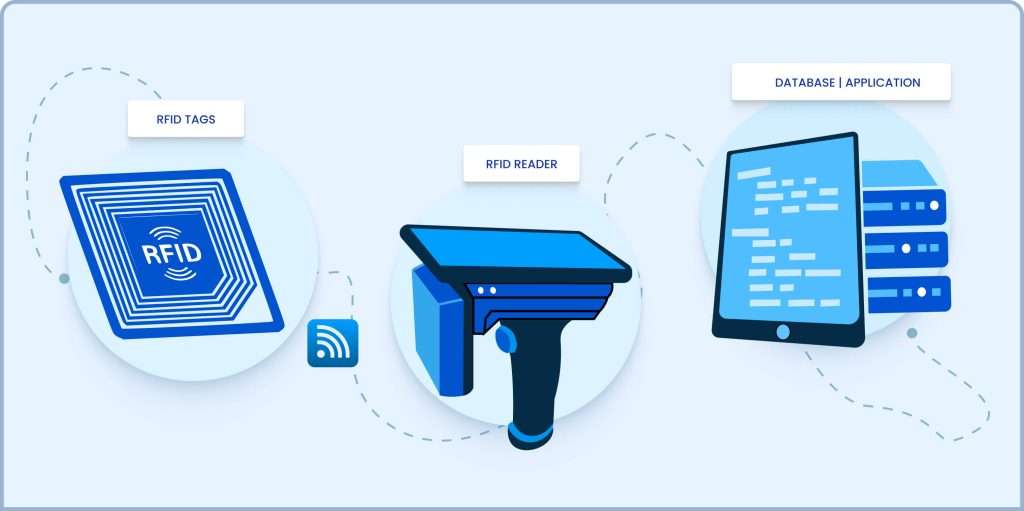
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is a type of wireless communication technology based on electromagnetic fields and is meant to transfer data between a reader and an electronic tag. As the majority of RFID tags are passive, i.e., do not have batteries, or active with a battery, each tag may memorize information about the object concerned, such as its identity, location, and other interesting facts. The major components of an RFID system consist of three:
RFID Tags: Item inventories are tagged and contain identifiers among other information.
RFID Readers: Equipments that send radio waves to interrogate RFID tags, read, and process the information.
Middleware: Software which is meant to collect RFID reader inputs, integrating them with inventory management systems.
Benefits of RFID in Inventory Management
1. High Accuracy and Efficiency
One of the most significant advantages of RFID technology is to improve the precision of one’s inventory. In comparison with barcode scanning, most traditional inventory management relies mainly on manual data entry, which is prone to errors. In contrast, real-time tracking is possible through RFID with items not requiring line-of-sight scanning. This results in fewer discrepancies and improved accuracy for inventory counts.
2. Real-Time Visibility
RF technology provides business owners with immediate visibility of the inventory levels, locations, and movements. In this regard, such transparency enhances effective decision-making and resource allocation. Businesses are always able to see what the stock levels are, where items are, and everything moving in or out of their inventory; hence they optimize supply chain processes.
3. Efficient Labor
RFID minimizes the need for manual counting and data entry since it automatically tracks inventory. This not only saves time but also allows staff to spend more quality time focusing on higher-value activities, such as customer service or strategic planning. Companies can work better with their operations, minimize labor costs, and maximize productivity with an RFID system.
4. Better Security
RFID technology enhances asset inventory security by checking on the assets in real-time. Businesses can put alerts on unauthorized movements or access, which helps prevent theft and losing tracks of assets. Further on, RFID tags can be made tamper-proof, thereby enhancing the security of your assets.
5. Improved Customer Satisfaction
With RFID technology, companies would be able to give the product availability and faster fulfillment of orders that would subsequently please customers.
Real-time inventory visibility enables businesses to respond quickly to any changing customer demand and preferences, thereby encouraging loyalty and repeat business.
Implementing RFID in Inventory Management
1. Assessing Business Needs
The specific inventory management requirements of a business need to be identified before applying RFID technology. This starts with the identification of pain points about stock discrepancies, inefficient processes, or security issues. Therefore, the business will know what type of RFID solution or system to apply in order to tackle their specific needs.
2. Choosing the Correct RFID System
Choosing the correct type of RFID system is actually a matter of exploring several different options, such as:
RFID Tags: Choose between active and passive tags depending on the characteristics and needs of your product.
RFID Readers: Choose fixed or handheld readers depending on your operational needs and environments.
Middleware Software: Ensure that the middleware software will interoperate easily with existing inventory management systems and provides sophisticated capability for data analytics.
3. Train Employees
Once the implementation process is over, the staff that will be using the system will require proper training. The training should encompass operation of the RFID reader, how data can be collected and analyzed, and troubleshooting of potential problems that may arise. Employee training investment will definitely result in easier adoption of the RFID solution with lesser disruption.
4. Pilot Program
The company should test the RFID system under controlled conditions through pilot programs before full-scale deployment. This is essential to identify potential issues, calibrate processes, and allow the assessment of the effectiveness of the system in enhancing the inventory management process.
5. Full Scale Deployment
Once the pilot testing is considered to be a success, companies can apply the solution on a massive scale. That would comprise installing RFID tags throughout the entire stock, readers at vantage points, and putting together the system with existing inventory management software.
Real-Life Applications of RFID for Inventory Control
1. Inventory Management in Retail
RFID in retail business changes business by enabling proper inventory management. Current giant retailers at present apply the use of RFID systems to enhance the accuracy of their inventories and facilitate their supply chain operations. When products are tagged with RFID tags, those companies can easily know the stock level and, therefore, reduce out-of-stocks incidents and enhance customers’ satisfaction.
2. Warehousing and Distribution
RFID technology is also causing ripples in warehousing and distribution centers. Companies like Amazon and Target use this facility to track the level of goods in warehouses and, hence, can optimize space usage effectively and arrange for a faster order fulfillment rate. These companies can ensure inventory tracking through automation, thus reducing labor costs and enabling time-bound delivery to customers.
3. Healthcare Inventory Management
Medical supply, equipment, and drugs have the application of RFID technology in the health sector. Their operations enable hospitals to reduce stockouts and expired drugs with RFID
systems. For example, Cleveland Clinic uses RFID technology in handling surgical instruments, reducing availability at the right time and thus fewer delays in performing surgeries.
4. Manufacturing and Asset Tracking
Companies are using RFID technology to track raw materials, parts, and finished products at every stage of the production process. This enhances visibility on levels of inventory as well as production schedules, making manufacturers better at running their operations and waste reduction. Boeing uses RFID to track aircraft parts to ensure availability for assembly so lead times are reduced.
The use of RFID technology provides real-time monitoring of inventory throughout the supply chain. This gives timely insight into where the inventory is, who is handling it, and when it will reach the end customers. This ensures that businesses maintain a clear view of their inventory from suppliers to customers, thus better enabling them to understand demand and eventually plan for much more efficient and effective inventory. For instance, Procter & Gamble has utilized RFID as a means of following product movements all through the supply chain to make operations much more efficient and responsive to market change.
Conclusion
RFID helps transform the way inventory management is accomplished by increasing accuracy, efficiency, and visibility of the whole supply chain. Since more and more firms are discovering the advantages of using RFID technology, the technology will also form a core part of the various strategies related to inventory management in industries.
If these companies carry out detailed requirement analysis, choose the right RFID system, and invest in training their employees, they are more likely to successfully integrate RFID solutions to help drive efficiency and increase customer satisfaction. The one thing most certain about the foreseeable future of inventory management is that the RFID technology will be crucial to the provision of supply chain operations going forward.